Evaluating Diversity in Automatic Poetry Generation
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2024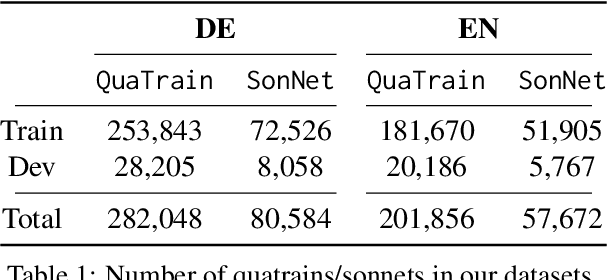
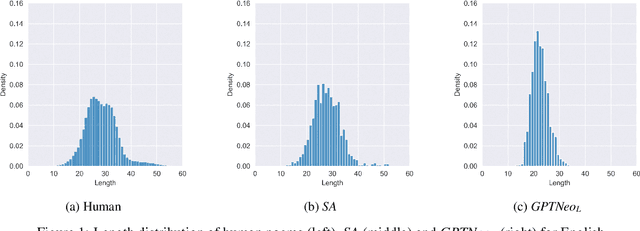
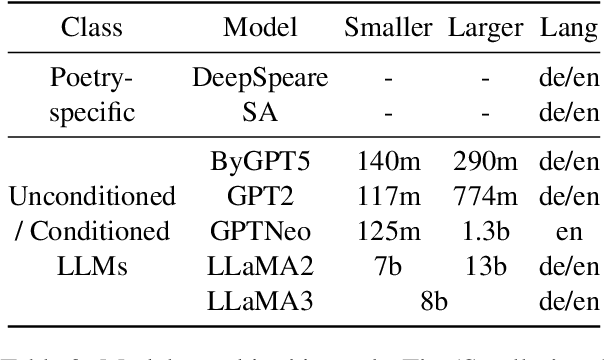
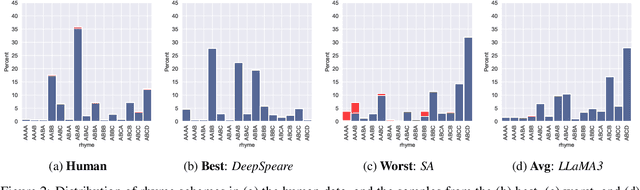
Natural Language Generation (NLG), and more generally generative AI, are among the currently most impactful research fields. Creative NLG, such as automatic poetry generation, is a fascinating niche in this area. While most previous research has focused on forms of the Turing test when evaluating automatic poetry generation - can humans distinguish between automatic and human generated poetry - we evaluate the diversity of automatically generated poetry, by comparing distributions of generated poetry to distributions of human poetry along structural, lexical, semantic and stylistic dimensions, assessing different model types (word vs. character-level, general purpose LLMs vs. poetry-specific models), including the very recent LLaMA3, and types of fine-tuning (conditioned vs. unconditioned). We find that current automatic poetry systems are considerably underdiverse along multiple dimensions - they often do not rhyme sufficiently, are semantically too uniform and even do not match the length distribution of human poetry. Our experiments reveal, however, that style-conditioning and character-level modeling clearly increases diversity across virtually all dimensions we explore. Our identified limitations may serve as the basis for more genuinely diverse future poetry generation models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge