Environment Perception Framework Fusing Multi-Object Tracking, Dynamic Occupancy Grid Maps and Digital Maps
Paper and Code
Dec 20, 2018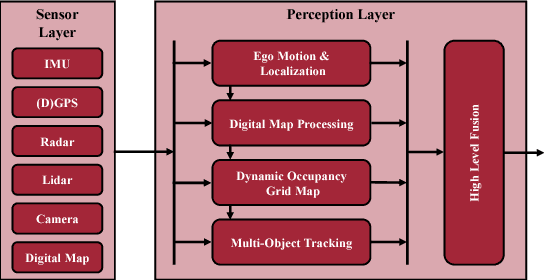
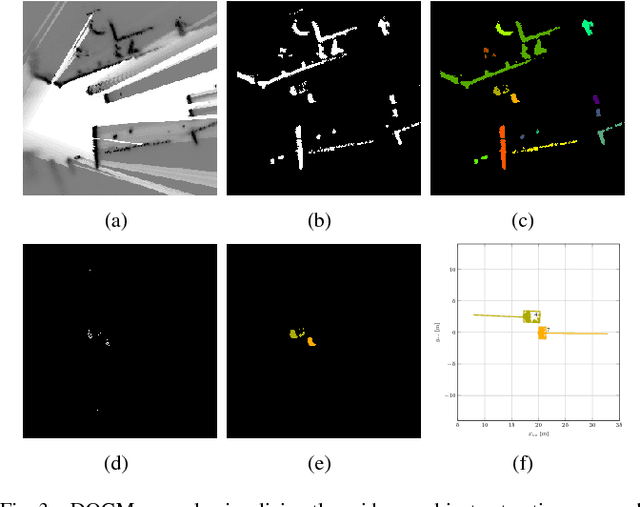
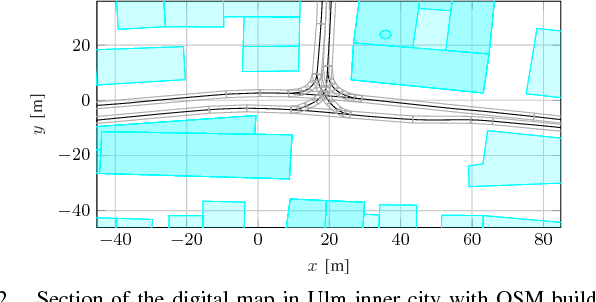

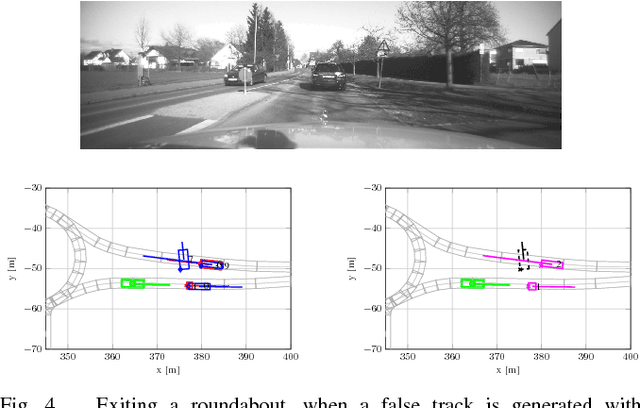
Autonomously driving vehicles require a complete and robust perception of the local environment. A main challenge is to perceive any other road users, where multi-object tracking or occupancy grid maps are commonly used. The presented approach combines both methods to compensate false positives and receive a complementary environment perception. Therefore, an environment perception framework is introduced that defines a common representation, extracts objects from a dynamic occupancy grid map and fuses them with tracks of a Labeled Multi-Bernoulli filter. Finally, a confidence value is developed, that validates object estimates using different constraints regarding physical possibilities, method specific characteristics and contextual information from a digital map. Experimental results with real world data highlight the robustness and significance of the presented fusing approach, utilizing the confidence value in rural and urban scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge