Ensemble of Convolution Neural Networks on Heterogeneous Signals for Sleep Stage Scoring
Paper and Code
Jul 23, 2021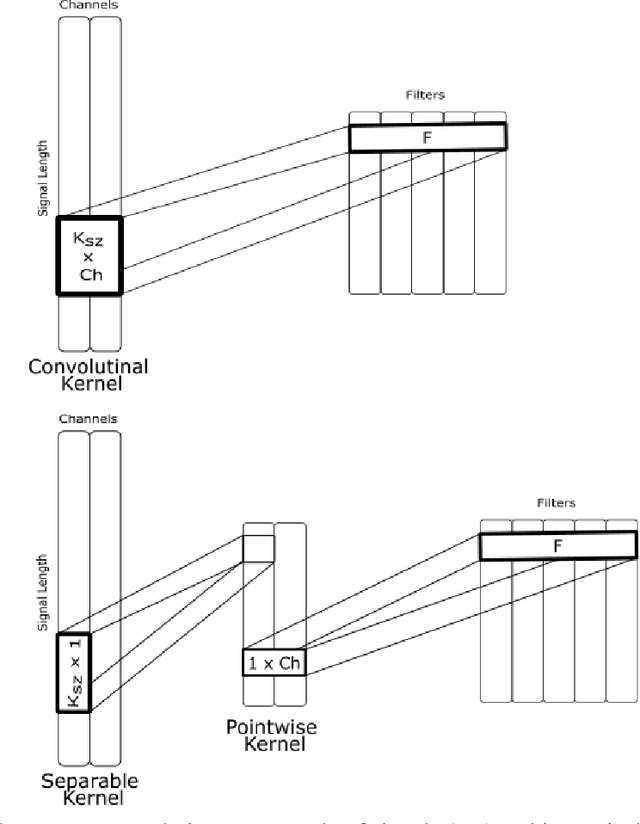
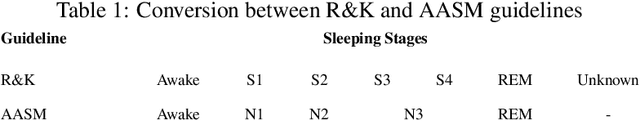
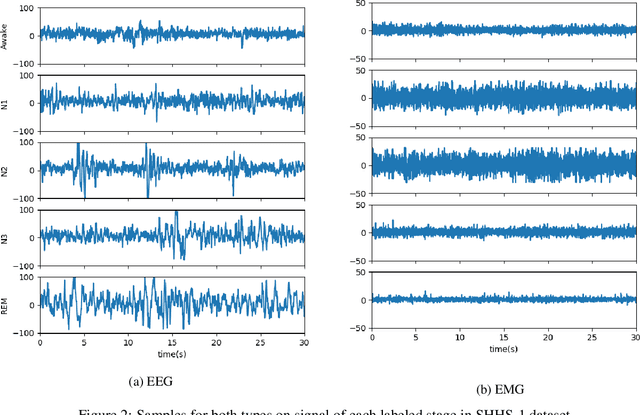
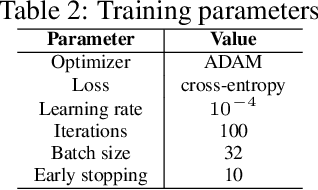
Over the years, several approaches have tried to tackle the problem of performing an automatic scoring of the sleeping stages. Although any polysomnography usually collects over a dozen of different signals, this particular problem has been mainly tackled by using only the Electroencephalograms presented in those records. On the other hand, the other recorded signals have been mainly ignored by most works. This paper explores and compares the convenience of using additional signals apart from electroencephalograms. More specifically, this work uses the SHHS-1 dataset with 5,804 patients containing an electromyogram recorded simultaneously as two electroencephalograms. To compare the results, first, the same architecture has been evaluated with different input signals and all their possible combinations. These tests show how, using more than one signal especially if they are from different sources, improves the results of the classification. Additionally, the best models obtained for each combination of one or more signals have been used in ensemble models and, its performance has been compared showing the convenience of using these multi-signal models to improve the classification. The best overall model, an ensemble of Depth-wise Separational Convolutional Neural Networks, has achieved an accuracy of 86.06\% with a Cohen's Kappa of 0.80 and a $F_{1}$ of 0.77. Up to date, those are the best results on the complete dataset and it shows a significant improvement in the precision and recall for the most uncommon class in the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge