Enhancing Generative Molecular Design via Uncertainty-guided Fine-tuning of Variational Autoencoders
Paper and Code
May 31, 2024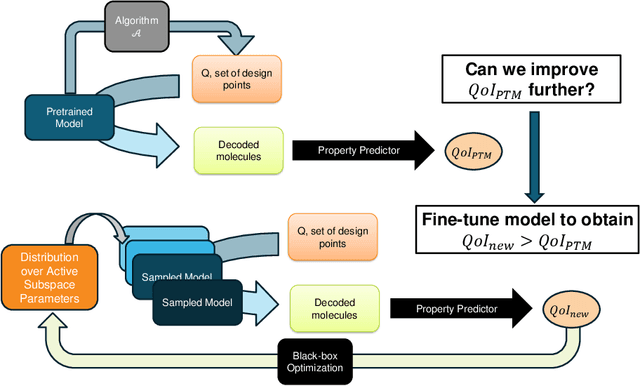
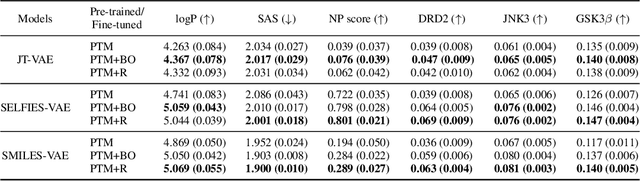
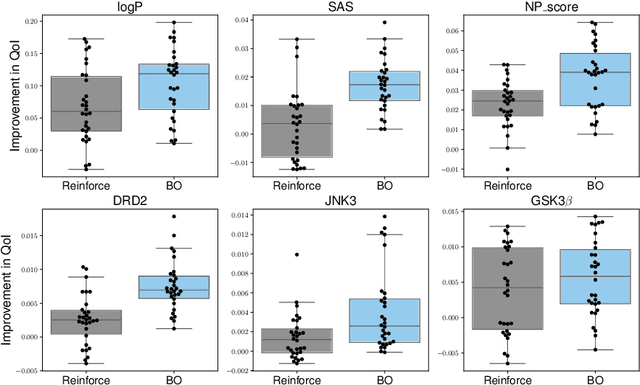
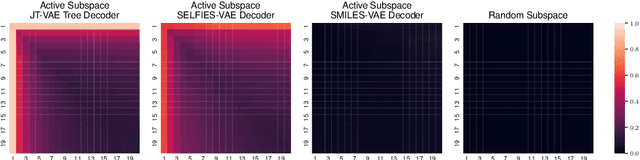
In recent years, deep generative models have been successfully adopted for various molecular design tasks, particularly in the life and material sciences. A critical challenge for pre-trained generative molecular design (GMD) models is to fine-tune them to be better suited for downstream design tasks aimed at optimizing specific molecular properties. However, redesigning and training an existing effective generative model from scratch for each new design task is impractical. Furthermore, the black-box nature of typical downstream tasks$\unicode{x2013}$such as property prediction$\unicode{x2013}$makes it nontrivial to optimize the generative model in a task-specific manner. In this work, we propose a novel approach for a model uncertainty-guided fine-tuning of a pre-trained variational autoencoder (VAE)-based GMD model through performance feedback in an active learning setting. The main idea is to quantify model uncertainty in the generative model, which is made efficient by working within a low-dimensional active subspace of the high-dimensional VAE parameters explaining most of the variability in the model's output. The inclusion of model uncertainty expands the space of viable molecules through decoder diversity. We then explore the resulting model uncertainty class via black-box optimization made tractable by low-dimensionality of the active subspace. This enables us to identify and leverage a diverse set of high-performing models to generate enhanced molecules. Empirical results across six target molecular properties, using multiple VAE-based generative models, demonstrate that our uncertainty-guided fine-tuning approach consistently outperforms the original pre-trained models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge