Enhancing Diversity in Bayesian Deep Learning via Hyperspherical Energy Minimization of CKA
Paper and Code
Oct 31, 2024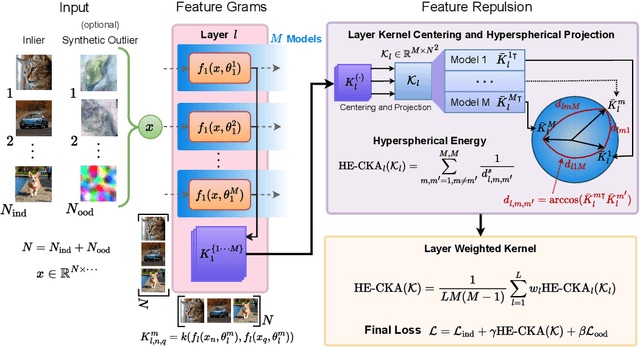
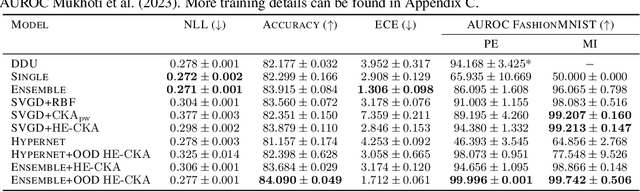
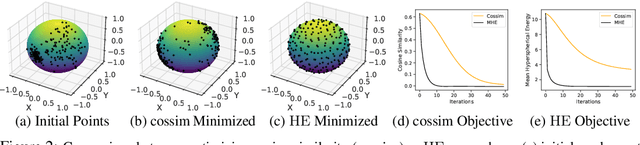
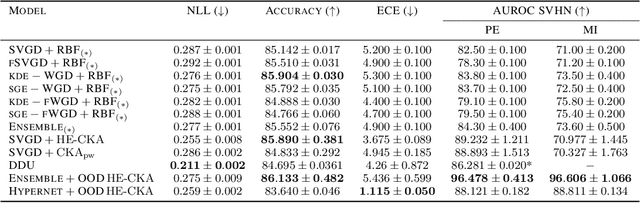
Particle-based Bayesian deep learning often requires a similarity metric to compare two networks. However, naive similarity metrics lack permutation invariance and are inappropriate for comparing networks. Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA) on feature kernels has been proposed to compare deep networks but has not been used as an optimization objective in Bayesian deep learning. In this paper, we explore the use of CKA in Bayesian deep learning to generate diverse ensembles and hypernetworks that output a network posterior. Noting that CKA projects kernels onto a unit hypersphere and that directly optimizing the CKA objective leads to diminishing gradients when two networks are very similar. We propose adopting the approach of hyperspherical energy (HE) on top of CKA kernels to address this drawback and improve training stability. Additionally, by leveraging CKA-based feature kernels, we derive feature repulsive terms applied to synthetically generated outlier examples. Experiments on both diverse ensembles and hypernetworks show that our approach significantly outperforms baselines in terms of uncertainty quantification in both synthetic and realistic outlier detection tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge