Enhancing Crowdsourced Audio for Text-to-Speech Models
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2024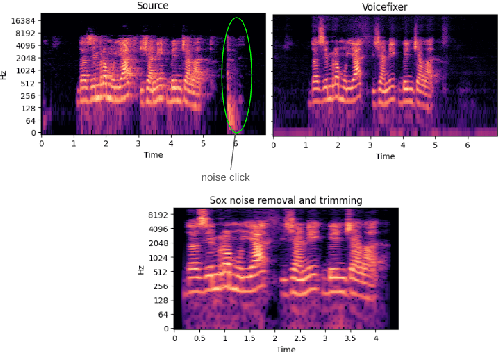
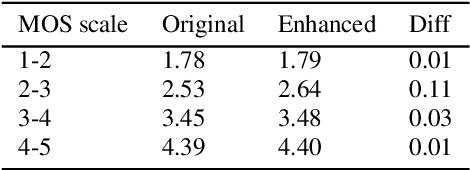
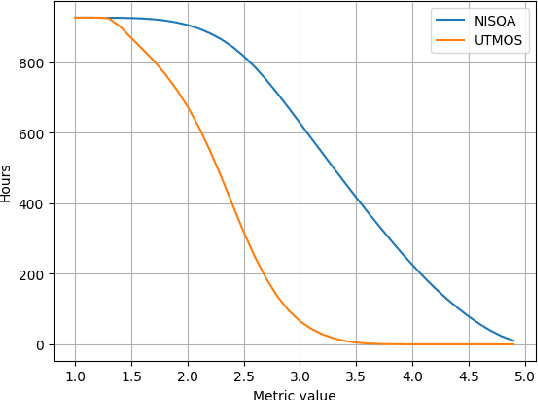

High-quality audio data is a critical prerequisite for training robust text-to-speech models, which often limits the use of opportunistic or crowdsourced datasets. This paper presents an approach to overcome this limitation by implementing a denoising pipeline on the Catalan subset of Commonvoice, a crowd-sourced corpus known for its inherent noise and variability. The pipeline incorporates an audio enhancement phase followed by a selective filtering strategy. We developed an automatic filtering mechanism leveraging Non-Intrusive Speech Quality Assessment (NISQA) models to identify and retain the highest quality samples post-enhancement. To evaluate the efficacy of this approach, we trained a state of the art diffusion-based TTS model on the processed dataset. The results show a significant improvement, with an increase of 0.4 in the UTMOS Score compared to the baseline dataset without enhancement. This methodology shows promise for expanding the utility of crowdsourced data in TTS applications, particularly for mid to low resource languages like Catalan.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge