Enforcing connectivity of 3D linear structures using their 2D projections
Paper and Code
Jul 14, 2022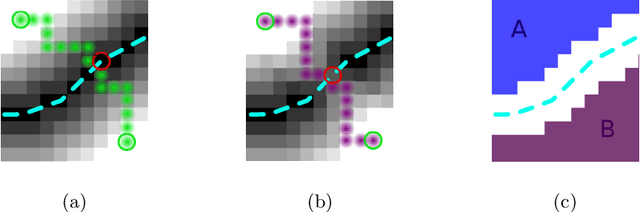
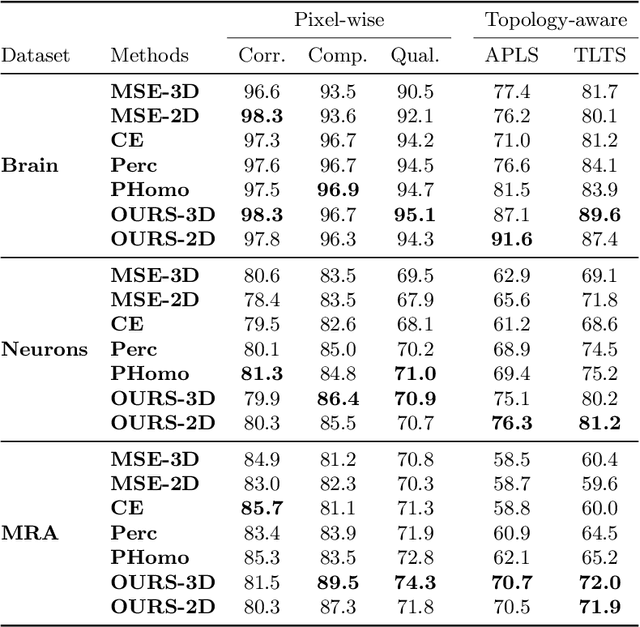
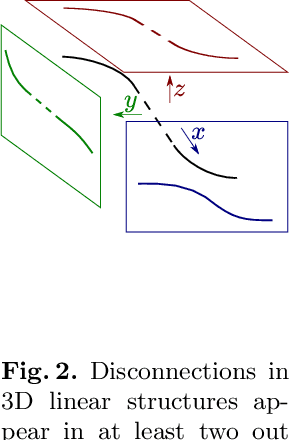
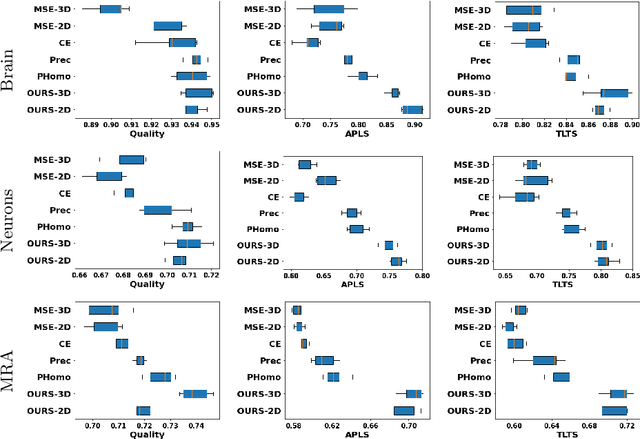
Many biological and medical tasks require the delineation of 3D curvilinear structures such as blood vessels and neurites from image volumes. This is typically done using neural networks trained by minimizing voxel-wise loss functions that do not capture the topological properties of these structures. As a result, the connectivity of the recovered structures is often wrong, which lessens their usefulness. In this paper, we propose to improve the 3D connectivity of our results by minimizing a sum of topology-aware losses on their 2D projections. This suffices to increase the accuracy and to reduce the annotation effort required to provide the required annotated training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge