Empirical Assessment of End-to-End Iris Recognition System Capacity
Paper and Code
Mar 20, 2023
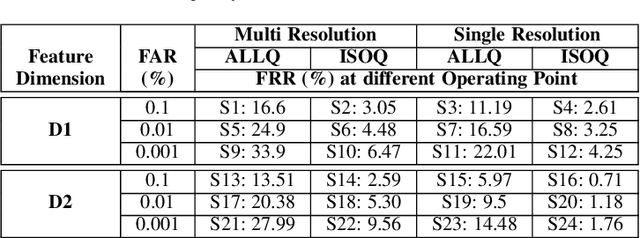

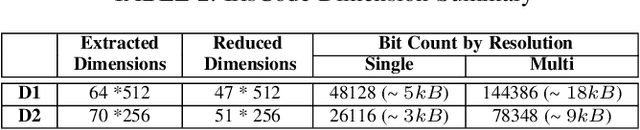
Iris is an established modality in biometric recognition applications including consumer electronics, e-commerce, border security, forensics, and de-duplication of identity at a national scale. In light of the expanding usage of biometric recognition, identity clash (when templates from two different people match) is an imperative factor of consideration for a system's deployment. This study explores system capacity estimation by empirically estimating the constrained capacity of an end-to-end iris recognition system (NIR systems with Daugman-based feature extraction) operating at an acceptable error rate i.e. the number of subjects a system can resolve before encountering an error. We study the impact of six system parameters on an iris recognition system's constrained capacity -- number of enrolled identities, image quality, template dimension, random feature elimination, filter resolution, and system operating point. In our assessment, we analyzed 13.2 million comparisons from 5158 unique identities for each of 24 different system configurations. This work provides a framework to better understand iris recognition system capacity as a function of biometric system configurations beyond the operating point, for large-scale applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge