ELMGS: Enhancing memory and computation scaLability through coMpression for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2024


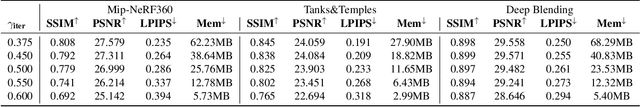
3D models have recently been popularized by the potentiality of end-to-end training offered first by Neural Radiance Fields and most recently by 3D Gaussian Splatting models. The latter has the big advantage of naturally providing fast training convergence and high editability. However, as the research around these is still in its infancy, there is still a gap in the literature regarding the model's scalability. In this work, we propose an approach enabling both memory and computation scalability of such models. More specifically, we propose an iterative pruning strategy that removes redundant information encoded in the model. We also enhance compressibility for the model by including in the optimization strategy a differentiable quantization and entropy coding estimator. Our results on popular benchmarks showcase the effectiveness of the proposed approach and open the road to the broad deployability of such a solution even on resource-constrained devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge