Elastica Models for Color Image Regularization
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2022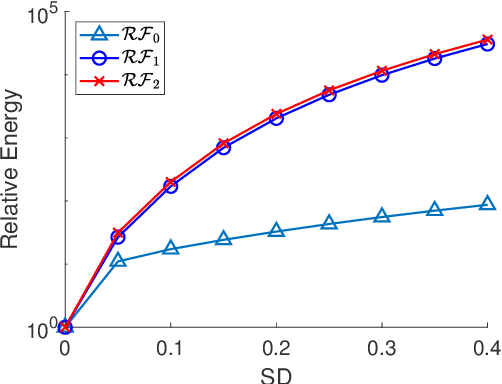
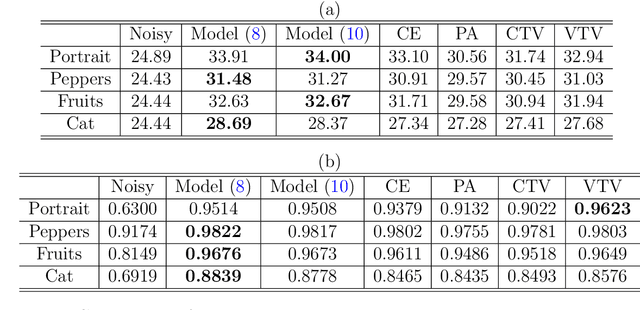

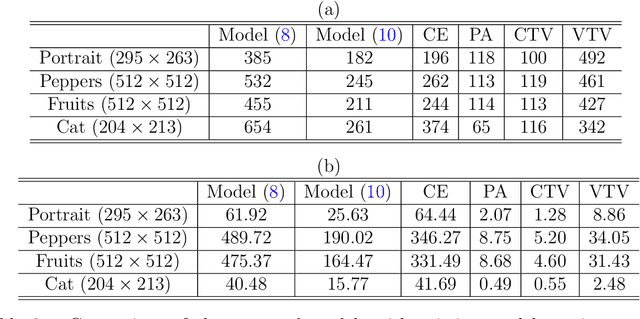
One classical approach to regularize color is to tream them as two dimensional surfaces embedded in a five dimensional spatial-chromatic space. In this case, a natural regularization term arises as the image surface area. Choosing the chromatic coordinates as dominating over the spatial ones, the image spatial coordinates could be thought of as a paramterization of the image surface manifold in a three dimensional color space. Minimizing the area of the image manifold leads to the Beltrami flow or mean curvature flow of the image surface in the 3D color space, while minimizing the elastica of the image surface yields an additional interesting regularization. Recently, the authors proposed a color elastica model, which minimizes both the surface area and elastica of the image manifold. In this paper, we propose to modify the color elastica and introduce two new models for color image regularization. The revised measures are motivated by the relations between the color elastica model, Euler's elastica model and the total variation model for gray level images. Compared to our previous color elastica model, the new models are direct extensions of Euler's elastica model to color images. The proposed models are nonlinear and challenging to minimize. To overcome this difficulty, two operator-splitting methods are suggested. Specifically, nonlinearities are decoupled by introducing new vector- and matrix-valued variables. Then, the minimization problems are converted to solving initial value problems which are time-discretized by operator splitting. Each subproblem, after splitting either, has a closed-form solution or can be solved efficiently. The effectiveness and advantages of the proposed models are demonstrated by comprehensive experiments. The benefits of incorporating the elastica of the image surface as regularization terms compared to common alternatives are empirically validated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge