Efficient Symbolic Planning with Views
Paper and Code
May 06, 2024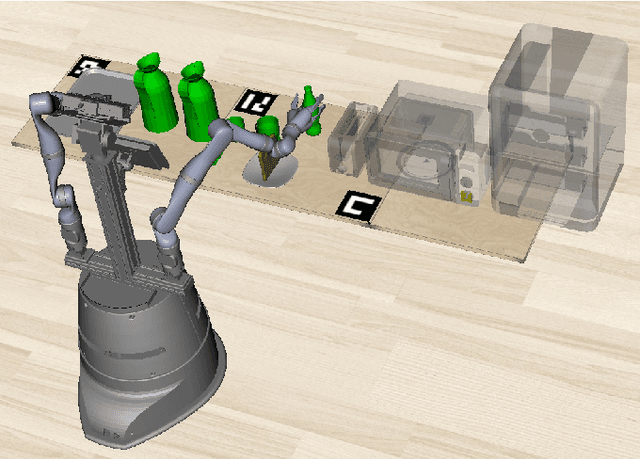

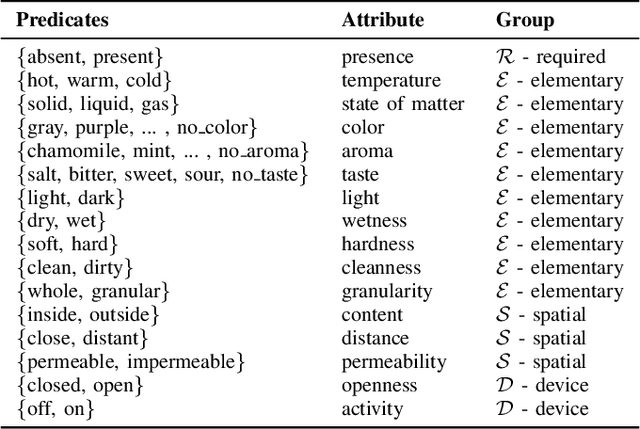
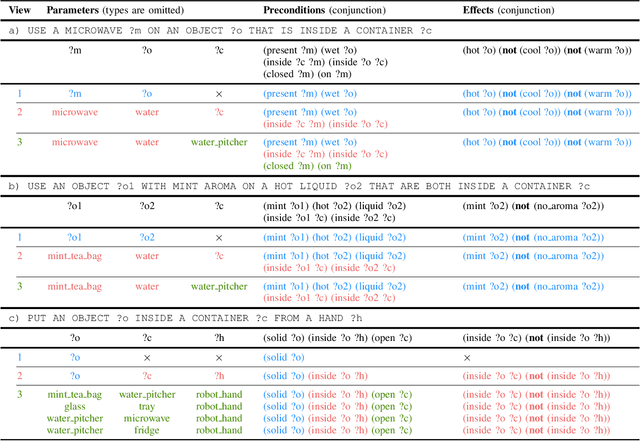
Robotic planning systems model spatial relations in detail as these are needed for manipulation tasks. In contrast to this, other physical attributes of objects and the effect of devices are usually oversimplified and expressed by abstract compound attributes. This limits the ability of planners to find alternative solutions. We propose to break these compound attributes down into a shared set of elementary attributes. This strongly facilitates generalization between different tasks and environments and thus helps to find innovative solutions. On the down-side, this generalization comes with an increased complexity of the solution space. Therefore, as the main contribution of the paper, we propose a method that splits the planning problem into a sequence of views, where in each view only an increasing subset of attributes is considered. We show that this view-based strategy offers a good compromise between planning speed and quality of the found plan, and discuss its general applicability and limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge