Edge-Compatible Reinforcement Learning for Recommendations
Paper and Code
Dec 10, 2021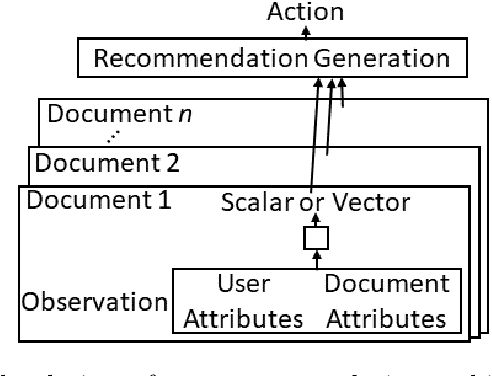
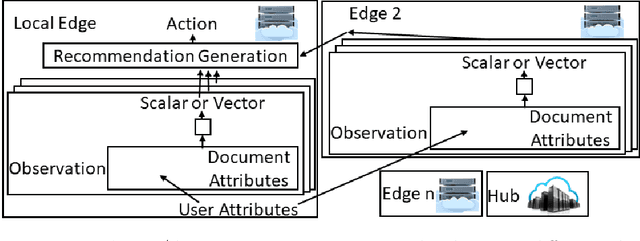
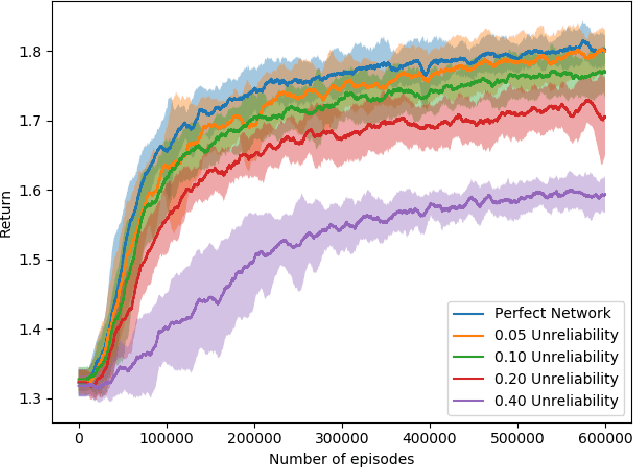
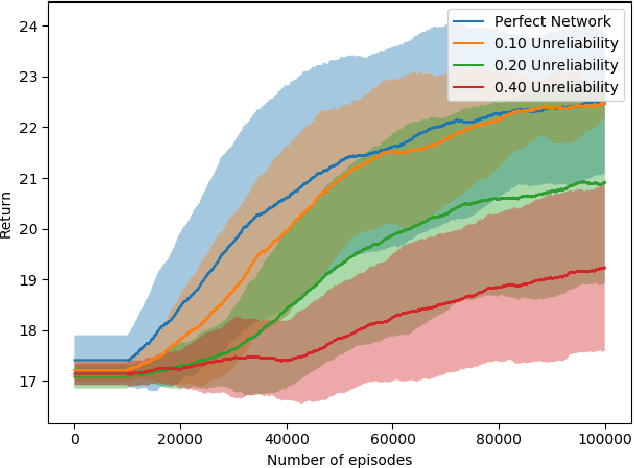
Most reinforcement learning (RL) recommendation systems designed for edge computing must either synchronize during recommendation selection or depend on an unprincipled patchwork collection of algorithms. In this work, we build on asynchronous coagent policy gradient algorithms \citep{kostas2020asynchronous} to propose a principled solution to this problem. The class of algorithms that we propose can be distributed over the internet and run asynchronously and in real-time. When a given edge fails to respond to a request for data with sufficient speed, this is not a problem; the algorithm is designed to function and learn in the edge setting, and network issues are part of this setting. The result is a principled, theoretically grounded RL algorithm designed to be distributed in and learn in this asynchronous environment. In this work, we describe this algorithm and a proposed class of architectures in detail, and demonstrate that they work well in practice in the asynchronous setting, even as the network quality degrades.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge