Dynamic Topological Data Analysis for Brain Networks via Wasserstein Graph Clustering
Paper and Code
Jan 11, 2022

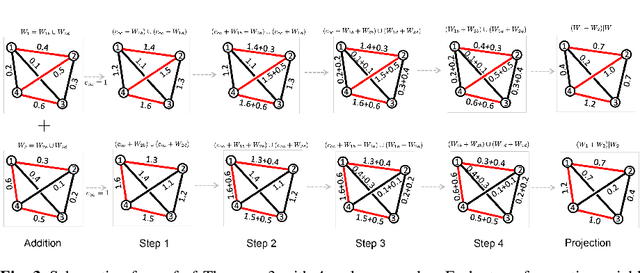

We present the novel Wasserstein graph clustering for dynamically changing graphs. The Wasserstein clustering penalizes the topological discrepancy between graphs. The Wasserstein clustering is shown to outperform the widely used k-means clustering. The method applied in more accurate determination of the state spaces of dynamically changing functional brain networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge