Dynamic Self-Consistency: Leveraging Reasoning Paths for Efficient LLM Sampling
Paper and Code
Aug 30, 2024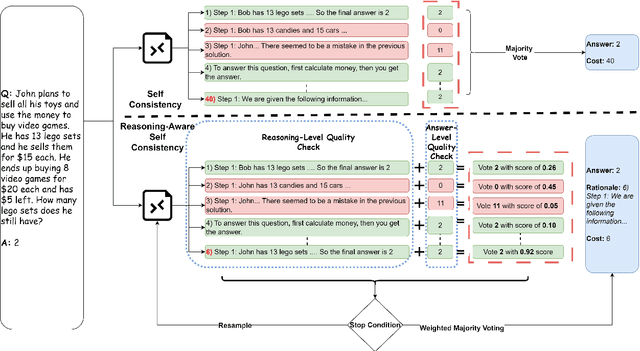
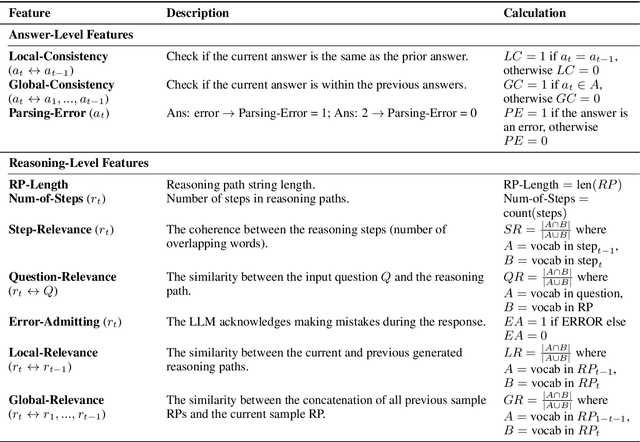
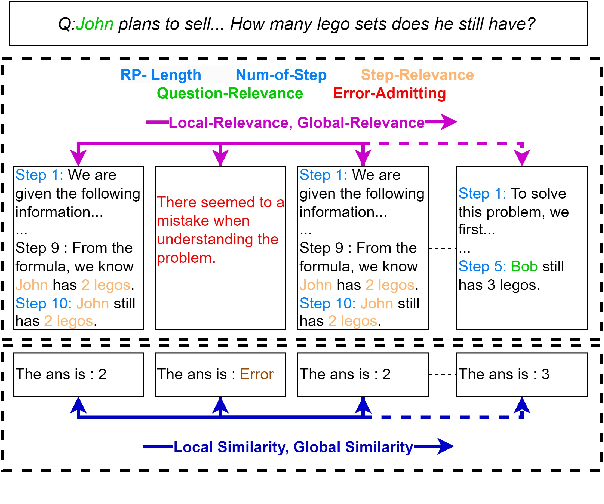
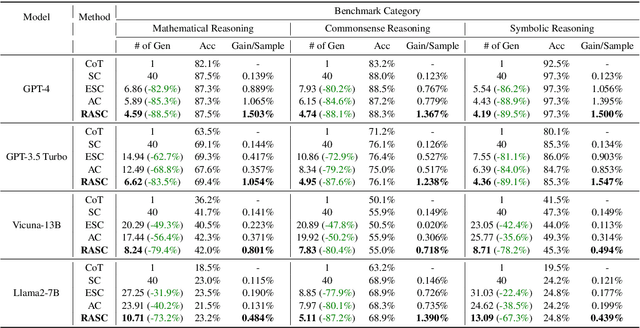
Self-Consistency (SC) is a widely used method to mitigate hallucinations in Large Language Models (LLMs) by sampling the LLM multiple times and outputting the most frequent solution. Despite its benefits, SC results in significant computational costs proportional to the number of samples generated. Previous early-stopping approaches, such as Early Stopping Self Consistency and Adaptive Consistency, have aimed to reduce these costs by considering output consistency, but they do not analyze the quality of the reasoning paths (RPs) themselves. To address this issue, we propose Reasoning-Aware Self-Consistency (RASC), an innovative early-stopping framework that dynamically adjusts the number of sample generations by considering both the output answer and the RPs from Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting. RASC assigns confidence scores sequentially to the generated samples, stops when certain criteria are met, and then employs weighted majority voting to optimize sample usage and enhance answer reliability. We comprehensively test RASC with multiple LLMs across varied QA datasets. RASC outperformed existing methods and significantly reduces sample usage by an average of 80% while maintaining or improving accuracy up to 5% compared to the original SC
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge