Dr-Vectors: Decision Residual Networks and an Improved Loss for Speaker Recognition
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2021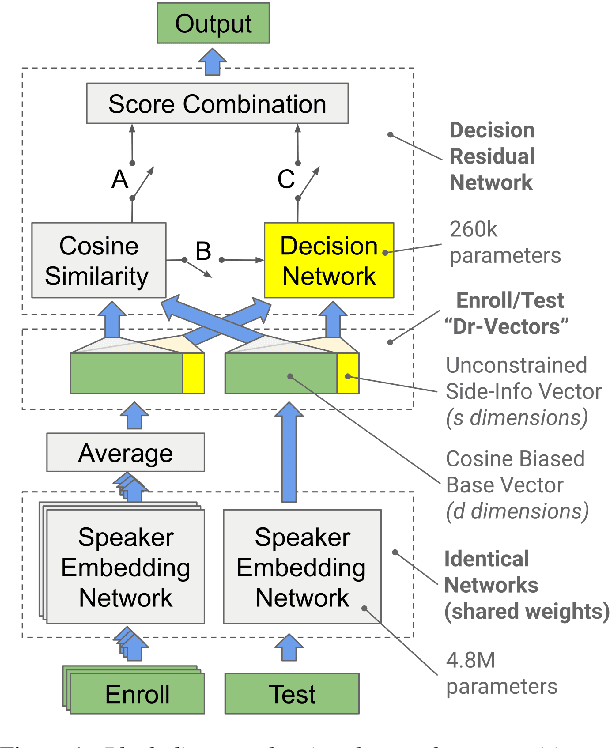
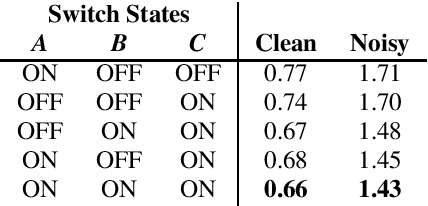
Many neural network speaker recognition systems model each speaker using a fixed-dimensional embedding vector. These embeddings are generally compared using either linear or 2nd-order scoring and, until recently, do not handle utterance-specific uncertainty. In this work we propose scoring these representations in a way that can capture uncertainty, enroll/test asymmetry and additional non-linear information. This is achieved by incorporating a 2nd-stage neural network (known as a decision network) as part of an end-to-end training regimen. In particular, we propose the concept of decision residual networks which involves the use of a compact decision network to leverage cosine scores and to model the residual signal that's needed. Additionally, we present a modification to the generalized end-to-end softmax loss function to better target the separation of same/different speaker scores. We observed significant performance gains for the two techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge