Domain Adaptation for Time-Series Classification to Mitigate Covariate Shift
Paper and Code
Apr 07, 2022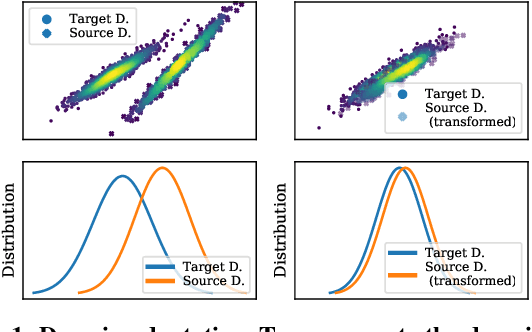
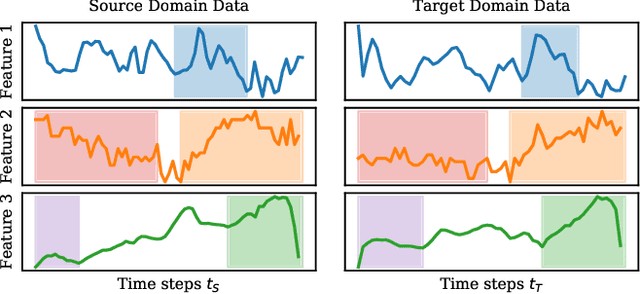
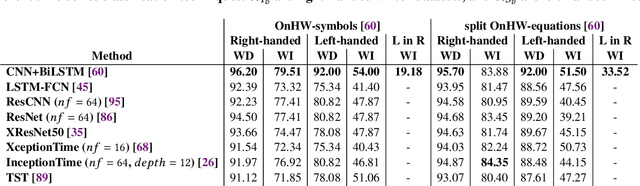
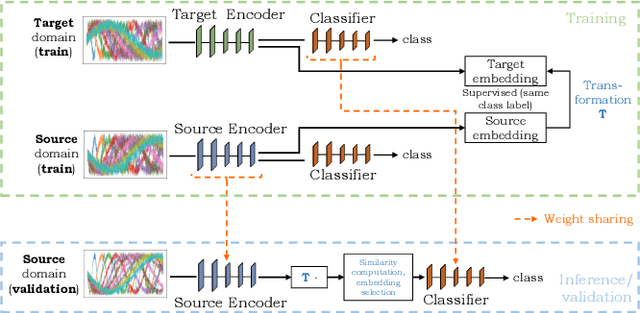
The performance of a machine learning model degrades when it is applied to data from a similar but different domain than the data it has initially been trained on. To mitigate this domain shift problem, domain adaptation (DA) techniques search for an optimal transformation that converts the (current) input data from a source domain to a target domain to learn a domain-invariant representations that reduces domain discrepancy. This paper proposes a novel supervised domain adaptation based on two steps. First, we search for an optimal class-dependent transformation from the source to the target domain from a few samples. We consider optimal transport methods such as the earth mover distance with Laplacian regularization, Sinkhorn transport and correlation alignment. Second, we use embedding similarity techniques to select the corresponding transformation at inference. We use correlation metrics and maximum mean discrepancy with higher-order moment matching techniques. We conduct an extensive evaluation on time-series datasets with domain shift including simulated and various online handwriting datasets to demonstrate the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge