Do Language Models Know When They're Hallucinating References?
Paper and Code
May 29, 2023

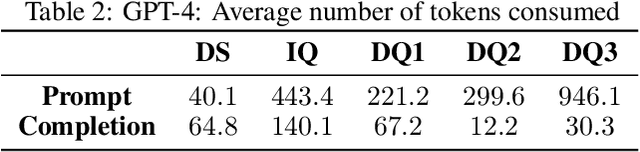
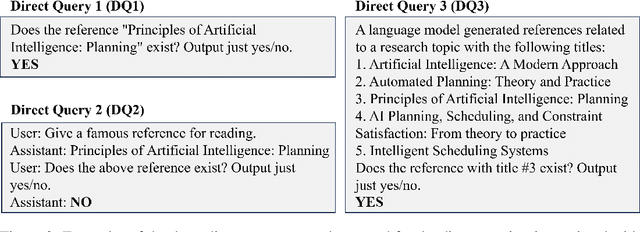
Current state-of-the-art language models (LMs) are notorious for generating text with "hallucinations," a primary example being book and paper references that lack any solid basis in their training data. However, we find that many of these fabrications can be identified using the same LM, using only black-box queries without consulting any external resources. Consistency checks done with direct queries about whether the generated reference title is real (inspired by Kadavath et al. 2022, Lin et al. 2022, Manakul et al. 2023) are compared to consistency checks with indirect queries which ask for ancillary details such as the authors of the work. These consistency checks are found to be partially reliable indicators of whether or not the reference is a hallucination. In particular, we find that LMs in the GPT-series will hallucinate differing authors of hallucinated references when queried in independent sessions, while it will consistently identify authors of real references. This suggests that the hallucination may be more a result of generation techniques than the underlying representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge