Do Deep Minds Think Alike? Selective Adversarial Attacks for Fine-Grained Manipulation of Multiple Deep Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2020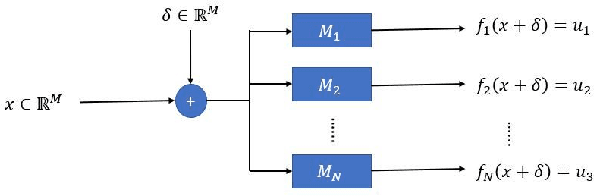
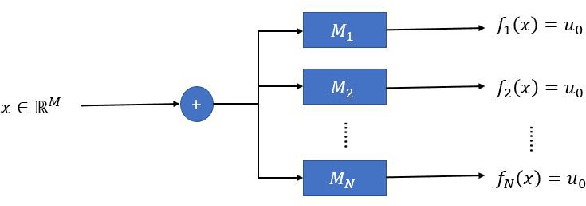
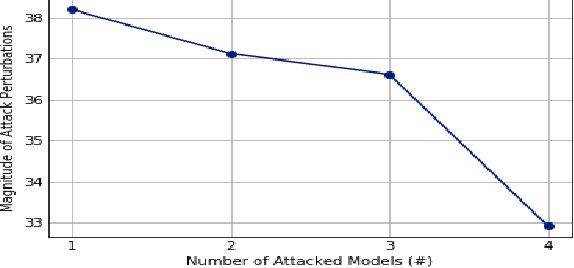
Recent works have demonstrated the existence of {\it adversarial examples} targeting a single machine learning system. In this paper we ask a simple but fundamental question of "selective fooling": given {\it multiple} machine learning systems assigned to solve the same classification problem and taking the same input signal, is it possible to construct a perturbation to the input signal that manipulates the outputs of these {\it multiple} machine learning systems {\it simultaneously} in arbitrary pre-defined ways? For example, is it possible to selectively fool a set of "enemy" machine learning systems but does not fool the other "friend" machine learning systems? The answer to this question depends on the extent to which these different machine learning systems "think alike". We formulate the problem of "selective fooling" as a novel optimization problem, and report on a series of experiments on the MNIST dataset. Our preliminary findings from these experiments show that it is in fact very easy to selectively manipulate multiple MNIST classifiers simultaneously, even when the classifiers are identical in their architectures, training algorithms and training datasets except for random initialization during training. This suggests that two nominally equivalent machine learning systems do not in fact "think alike" at all, and opens the possibility for many novel applications and deeper understandings of the working principles of deep neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge