Do Chinese models speak Chinese languages?
Paper and Code
Mar 31, 2025
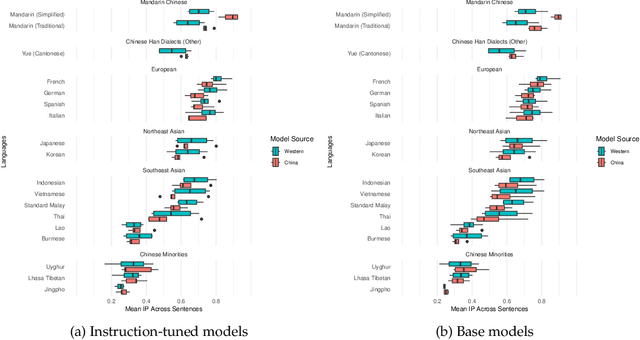


The release of top-performing open-weight LLMs has cemented China's role as a leading force in AI development. Do these models support languages spoken in China? Or do they speak the same languages as Western models? Comparing multilingual capabilities is important for two reasons. First, language ability provides insights into pre-training data curation, and thus into resource allocation and development priorities. Second, China has a long history of explicit language policy, varying between inclusivity of minority languages and a Mandarin-first policy. To test whether Chinese LLMs today reflect an agenda about China's languages, we test performance of Chinese and Western open-source LLMs on Asian regional and Chinese minority languages. Our experiments on Information Parity and reading comprehension show Chinese models' performance across these languages correlates strongly (r=0.93) with Western models', with the sole exception being better Mandarin. Sometimes, Chinese models cannot identify languages spoken by Chinese minorities such as Kazakh and Uyghur, even though they are good at French and German. These results provide a window into current development priorities, suggest options for future development, and indicate guidance for end users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge