Distributed learning with compressed gradients
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2018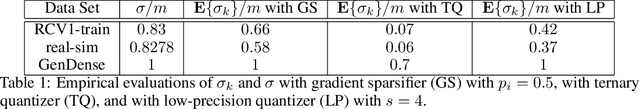
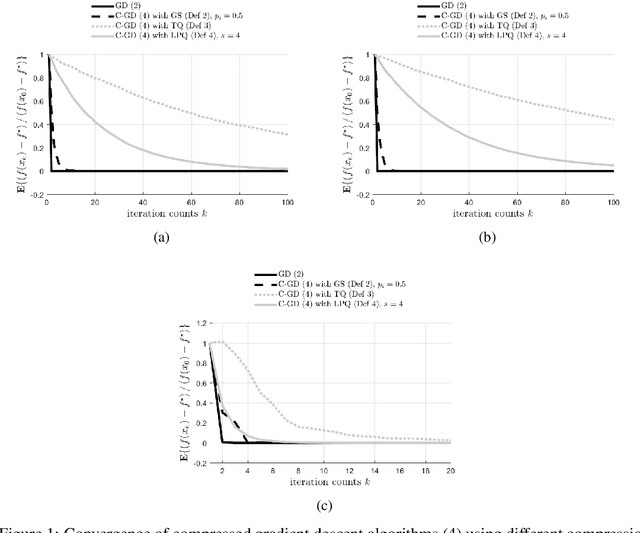
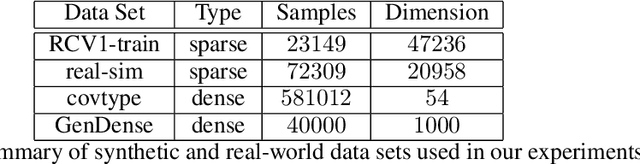
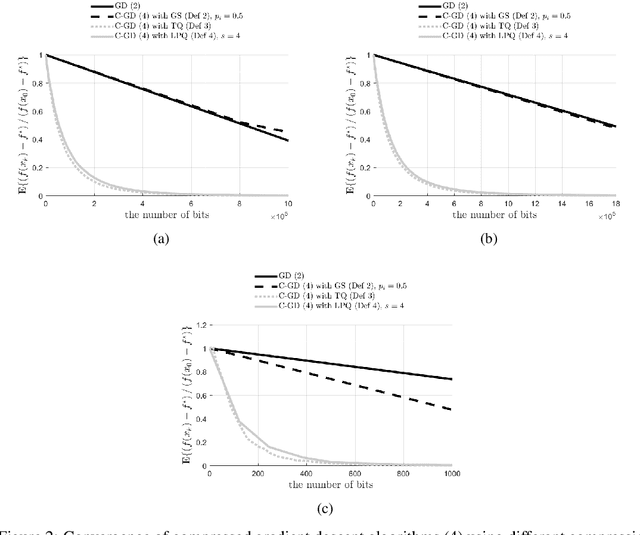
Asynchronous computation and gradient compression have emerged as two key techniques for achieving scalability in distributed optimization for large-scale machine learning. This paper presents a unified analysis framework for distributed gradient methods operating with staled and compressed gradients. Non-asymptotic bounds on convergence rates and information exchange are derived for several optimization algorithms. These bounds give explicit expressions for step-sizes and characterize how the amount of asynchrony and the compression accuracy affect iteration and communication complexity guarantees. Numerical results highlight convergence properties of different gradient compression algorithms and confirm that fast convergence under limited information exchange is indeed possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge