Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning for Functional Split Control in Energy Harvesting Virtualized Small Cells
Paper and Code
Aug 07, 2020
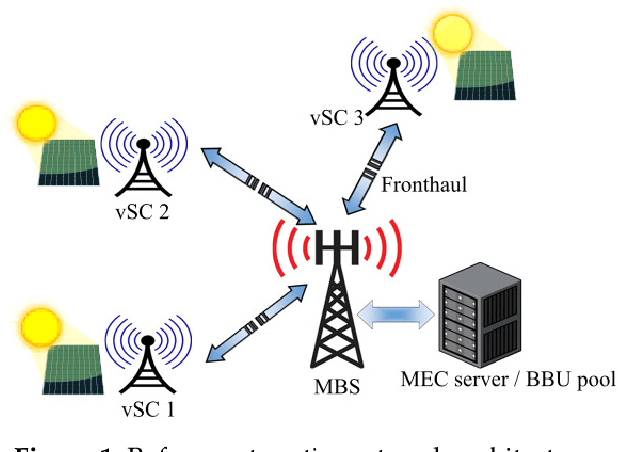
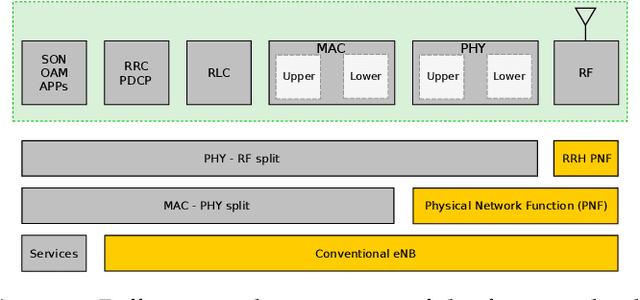
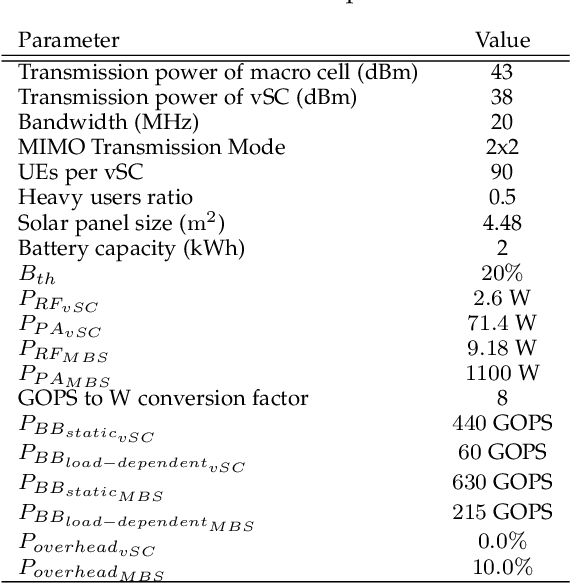
To meet the growing quest for enhanced network capacity, mobile network operators (MNOs) are deploying dense infrastructures of small cells. This, in turn, increases the power consumption of mobile networks, thus impacting the environment. As a result, we have seen a recent trend of powering mobile networks with harvested ambient energy to achieve both environmental and cost benefits. In this paper, we consider a network of virtualized small cells (vSCs) powered by energy harvesters and equipped with rechargeable batteries, which can opportunistically offload baseband (BB) functions to a grid-connected edge server depending on their energy availability. We formulate the corresponding grid energy and traffic drop rate minimization problem, and propose a distributed deep reinforcement learning (DDRL) solution. Coordination among vSCs is enabled via the exchange of battery state information. The evaluation of the network performance in terms of grid energy consumption and traffic drop rate confirms that enabling coordination among the vSCs via knowledge exchange achieves a performance close to the optimal. Numerical results also confirm that the proposed DDRL solution provides higher network performance, better adaptation to the changing environment, and higher cost savings with respect to a tabular multi-agent reinforcement learning (MRL) solution used as a benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge