Distilling Black-Box Travel Mode Choice Model for Behavioral Interpretation
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2019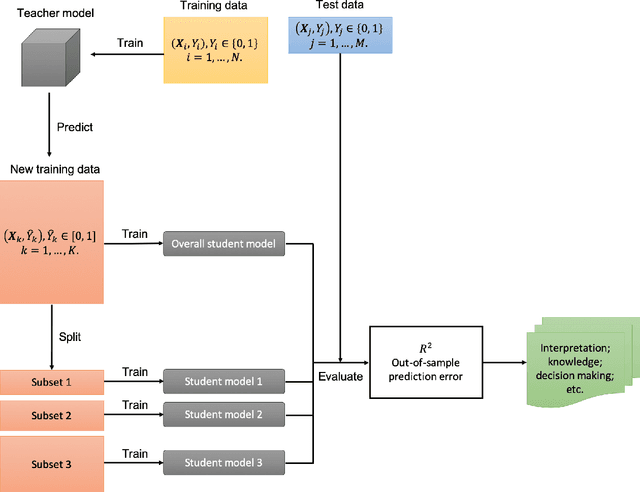
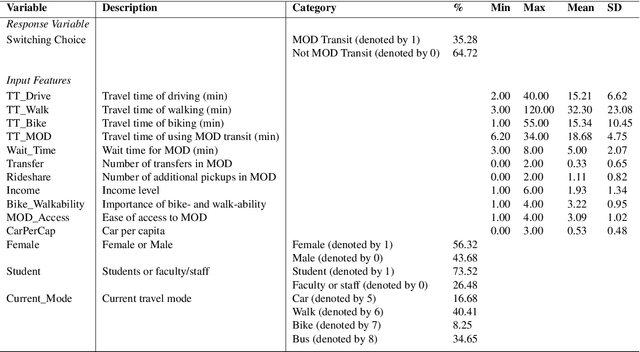
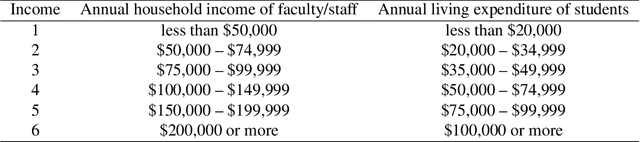
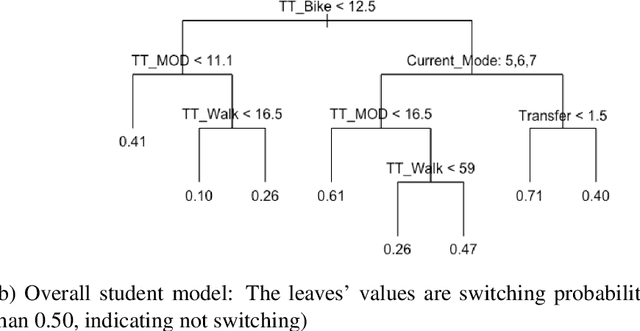
Machine learning has proved to be very successful for making predictions in travel behavior modeling. However, most machine-learning models have complex model structures and offer little or no explanation as to how they arrive at these predictions. Interpretations about travel behavior models are essential for decision makers to understand travelers' preferences and plan policy interventions accordingly. Therefore, this paper proposes to apply and extend the model distillation approach, a model-agnostic machine-learning interpretation method, to explain how a black-box travel mode choice model makes predictions for the entire population and subpopulations of interest. Model distillation aims at compressing knowledge from a complex model (teacher) into an understandable and interpretable model (student). In particular, the paper integrates model distillation with market segmentation to generate more insights by accounting for heterogeneity. Furthermore, the paper provides a comprehensive comparison of student models with the benchmark model (decision tree) and the teacher model (gradient boosting trees) to quantify the fidelity and accuracy of the students' interpretations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge