Discretization Error of Fourier Neural Operators
Paper and Code
May 03, 2024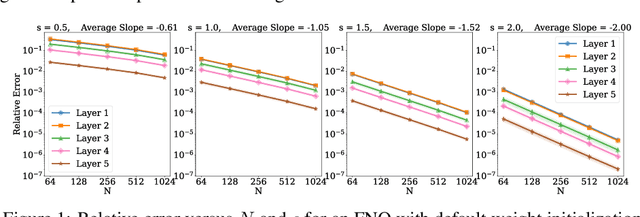
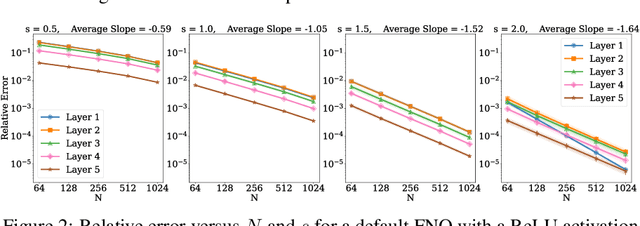
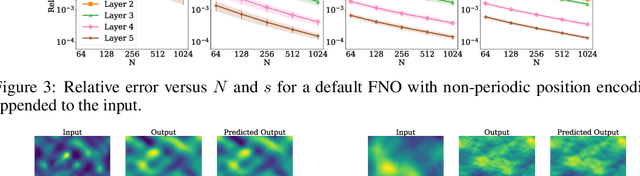
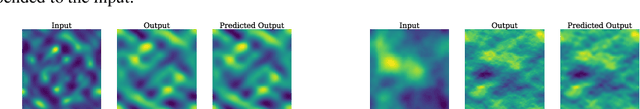
Operator learning is a variant of machine learning that is designed to approximate maps between function spaces from data. The Fourier Neural Operator (FNO) is a common model architecture used for operator learning. The FNO combines pointwise linear and nonlinear operations in physical space with pointwise linear operations in Fourier space, leading to a parameterized map acting between function spaces. Although FNOs formally involve convolutions of functions on a continuum, in practice the computations are performed on a discretized grid, allowing efficient implementation via the FFT. In this paper, the aliasing error that results from such a discretization is quantified and algebraic rates of convergence in terms of the grid resolution are obtained as a function of the regularity of the input. Numerical experiments that validate the theory and describe model stability are performed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge