Discovery Radiomics with CLEAR-DR: Interpretable Computer Aided Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Paper and Code
Oct 29, 2017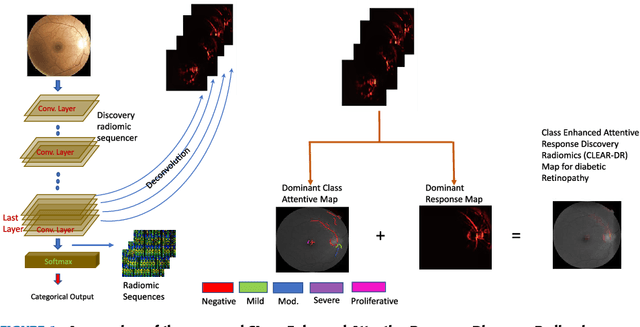
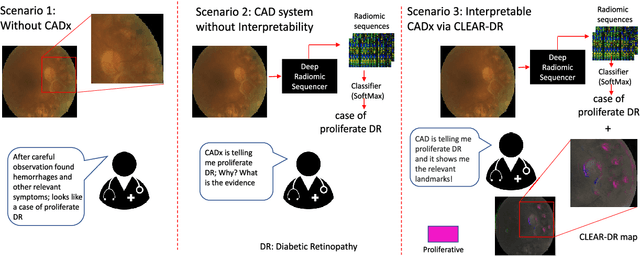
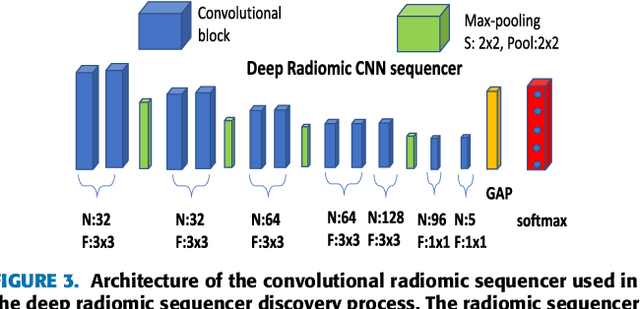
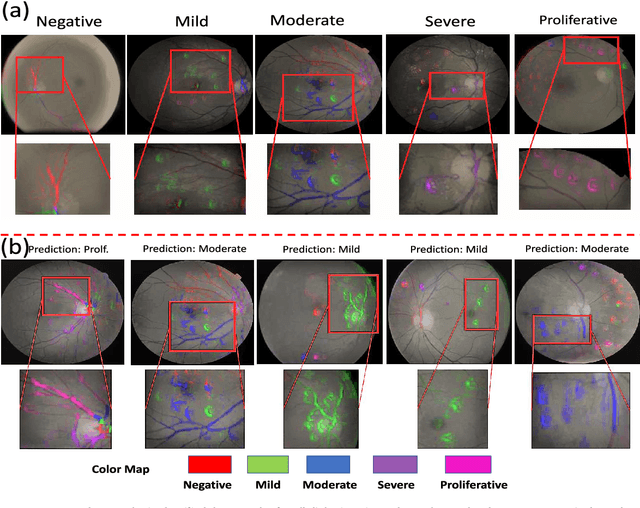
Objective: Radiomics-driven Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) has shown considerable promise in recent years as a potential tool for improving clinical decision support in medical oncology, particularly those based around the concept of Discovery Radiomics, where radiomic sequencers are discovered through the analysis of medical imaging data. One of the main limitations with current CAD approaches is that it is very difficult to gain insight or rationale as to how decisions are made, thus limiting their utility to clinicians. Methods: In this study, we propose CLEAR-DR, a novel interpretable CAD system based on the notion of CLass-Enhanced Attentive Response Discovery Radiomics for the purpose of clinical decision support for diabetic retinopathy. Results: In addition to disease grading via the discovered deep radiomic sequencer, the CLEAR-DR system also produces a visual interpretation of the decision-making process to provide better insight and understanding into the decision-making process of the system. Conclusion: We demonstrate the effectiveness and utility of the proposed CLEAR-DR system of enhancing the interpretability of diagnostic grading results for the application of diabetic retinopathy grading. Significance: CLEAR-DR can act as a potential powerful tool to address the uninterpretability issue of current CAD systems, thus improving their utility to clinicians.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge