Diffusion State Distances: Multitemporal Analysis, Fast Algorithms, and Applications to Biological Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2020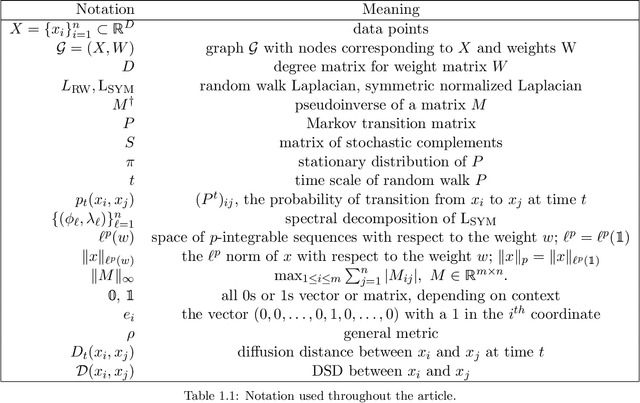
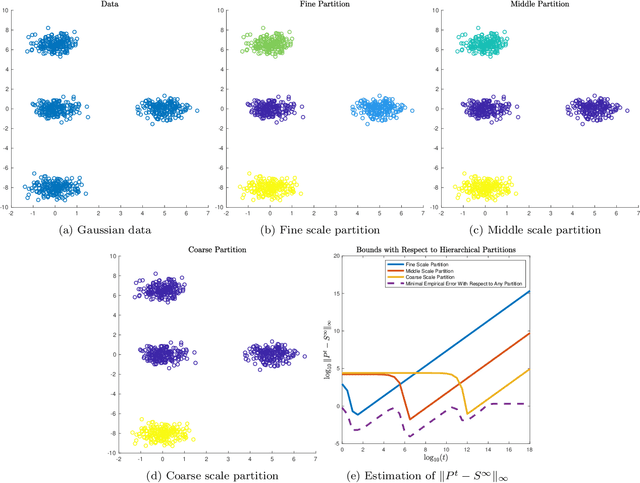
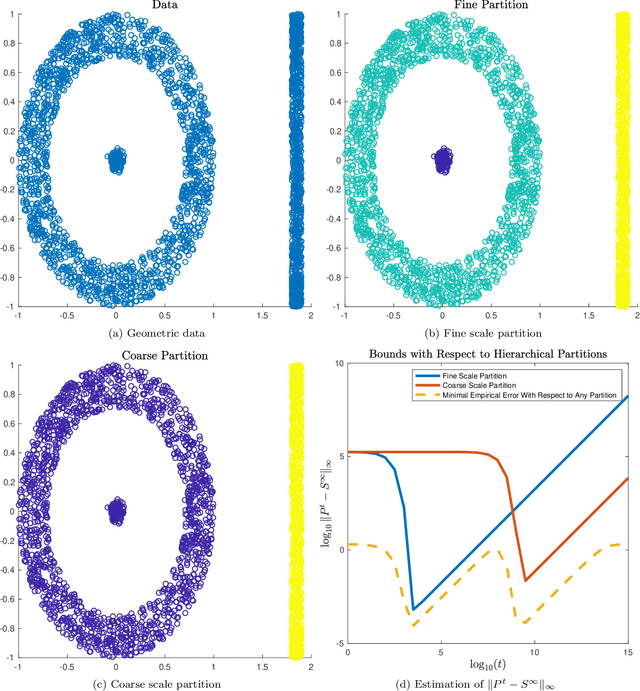
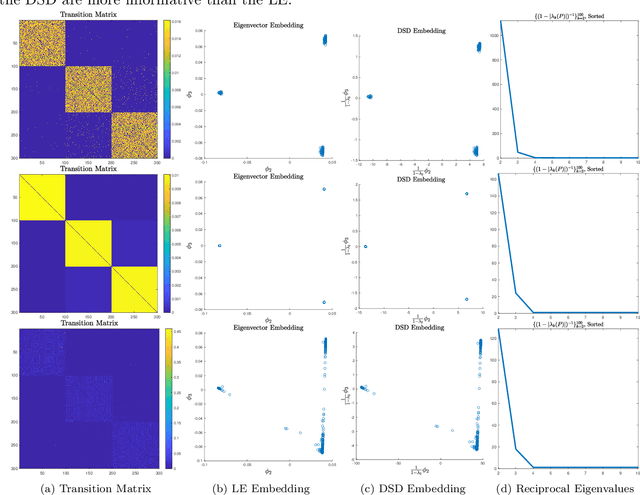
Data-dependent metrics are powerful tools for learning the underlying structure of high-dimensional data. This article develops and analyzes a data-dependent metric known as diffusion state distance (DSD), which compares points using a data-driven diffusion process. Unlike related diffusion methods, DSDs incorporate information across time scales, which allows for the intrinsic data structure to be inferred in a parameter-free manner. This article develops a theory for DSD based on the multitemporal emergence of mesoscopic equilibria in the underlying diffusion process. New algorithms for denoising and dimension reduction with DSD are also proposed and analyzed. These approaches are based on a weighted spectral decomposition of the underlying diffusion process, and experiments on synthetic datasets and real biological networks illustrate the efficacy of the proposed algorithms in terms of both speed and accuracy. Throughout, comparisons with related methods are made, in order to illustrate the distinct advantages of DSD for datasets exhibiting multiscale structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge