Differential Bias: On the Perceptibility of Stance Imbalance in Argumentation
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2022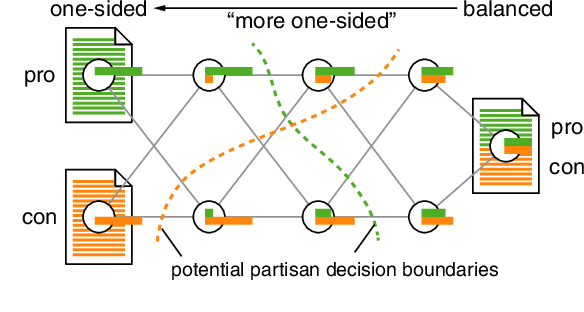
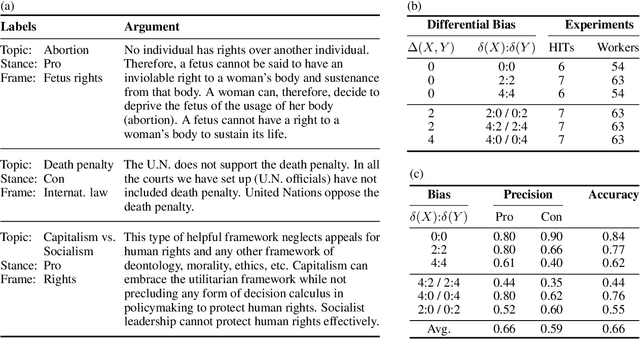
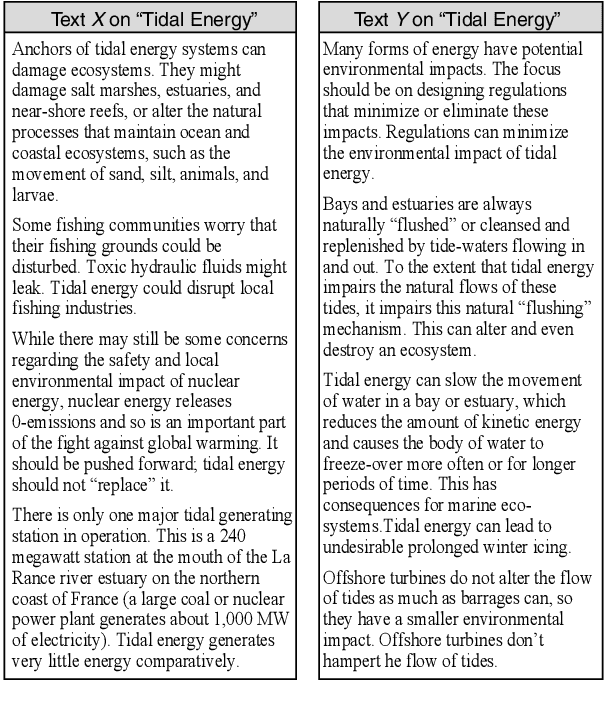
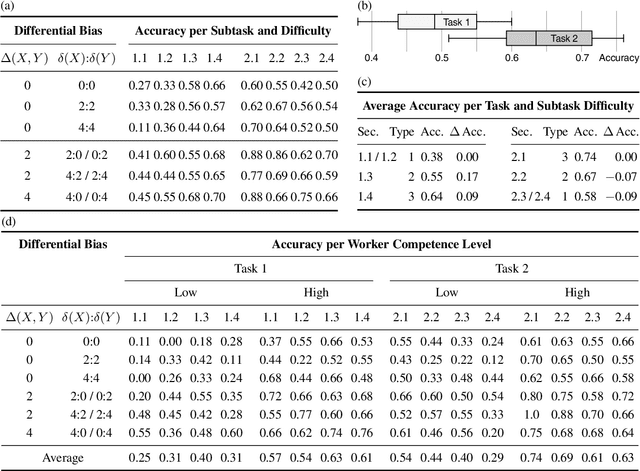
Most research on natural language processing treats bias as an absolute concept: Based on a (probably complex) algorithmic analysis, a sentence, an article, or a text is classified as biased or not. Given the fact that for humans the question of whether a text is biased can be difficult to answer or is answered contradictory, we ask whether an "absolute bias classification" is a promising goal at all. We see the problem not in the complexity of interpreting language phenomena but in the diversity of sociocultural backgrounds of the readers, which cannot be handled uniformly: To decide whether a text has crossed the proverbial line between non-biased and biased is subjective. By asking "Is text X more [less, equally] biased than text Y?" we propose to analyze a simpler problem, which, by its construction, is rather independent of standpoints, views, or sociocultural aspects. In such a model, bias becomes a preference relation that induces a partial ordering from least biased to most biased texts without requiring a decision on where to draw the line. A prerequisite for this kind of bias model is the ability of humans to perceive relative bias differences in the first place. In our research, we selected a specific type of bias in argumentation, the stance bias, and designed a crowdsourcing study showing that differences in stance bias are perceptible when (light) support is provided through training or visual aid.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge