Developing, Analyzing, and Evaluating Self-Drive Algorithms Using Drive-by-Wire Electric Vehicles
Paper and Code
Sep 04, 2024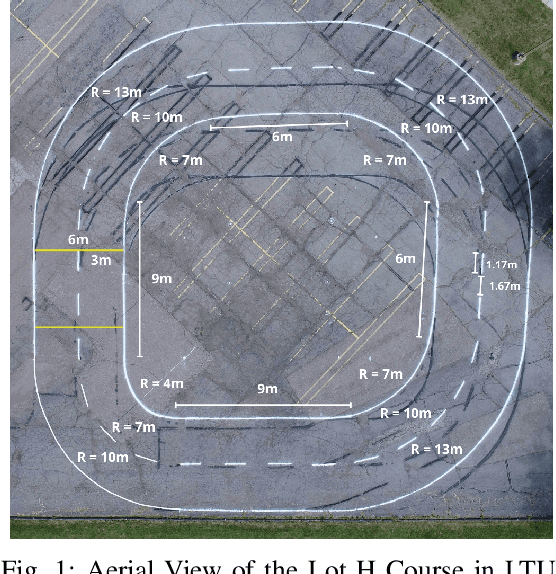
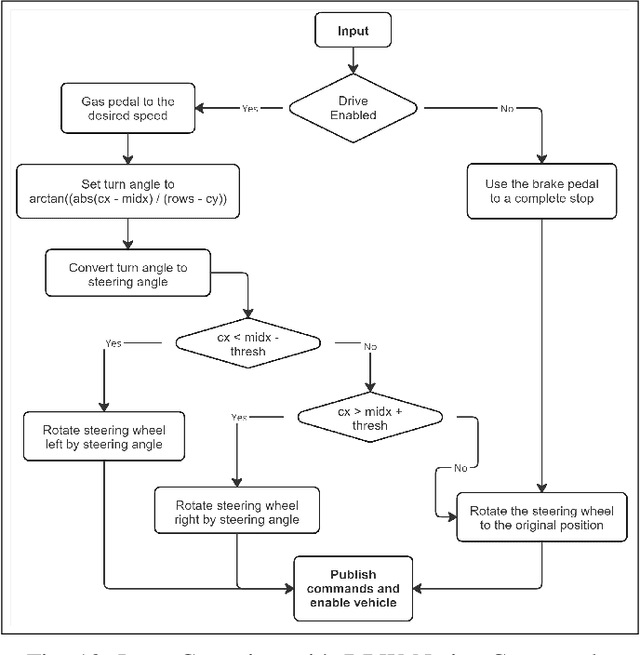
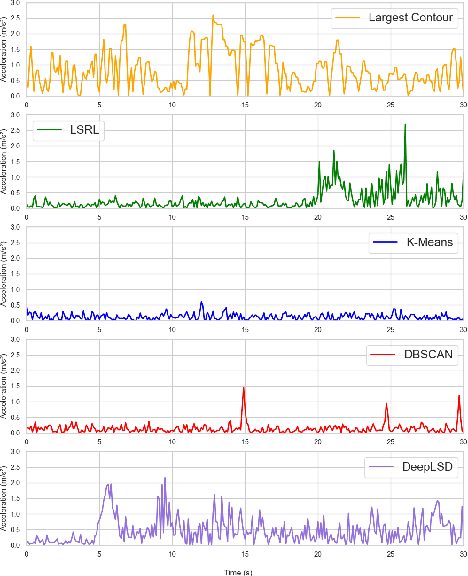
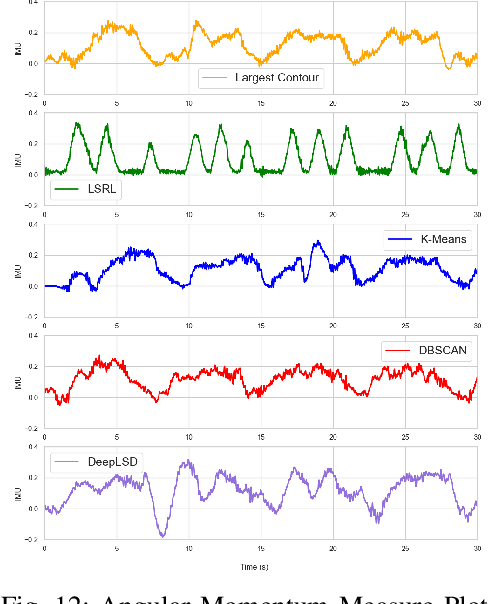
Reliable lane-following algorithms are essential for safe and effective autonomous driving. This project was primarily focused on developing and evaluating different lane-following programs to find the most reliable algorithm for a Vehicle to Everything (V2X) project. The algorithms were first tested on a simulator and then with real vehicles equipped with a drive-by-wire system using ROS (Robot Operating System). Their performance was assessed through reliability, comfort, speed, and adaptability metrics. The results show that the two most reliable approaches detect both lane lines and use unsupervised learning to separate them. These approaches proved to be robust in various driving scenarios, making them suitable candidates for integration into the V2X project.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge