Developing a Hybrid Data-Driven, Mechanistic Virtual Flow Meter -- a Case Study
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2020
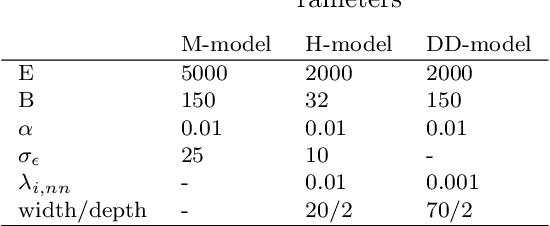
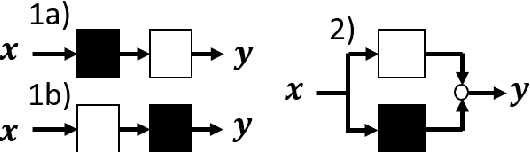
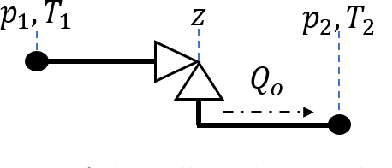
Virtual flow meters, mathematical models predicting production flow rates in petroleum assets, are useful aids in production monitoring and optimization. Mechanistic models based on first-principles are most common, however, data-driven models exploiting patterns in measurements are gaining popularity. This research investigates a hybrid modeling approach, utilizing techniques from both the aforementioned areas of expertise, to model a well production choke. The choke is represented with a simplified set of first-principle equations and a neural network to estimate the valve flow coefficient. Historical production data from the petroleum platform Edvard Grieg is used for model validation. Additionally, a mechanistic and a data-driven model are constructed for comparison of performance. A practical framework for development of models with varying degree of hybridity and stochastic optimization of its parameters is established. Results of the hybrid model performance are promising albeit with considerable room for improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge