Deterministic Gaussian Averaged Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2020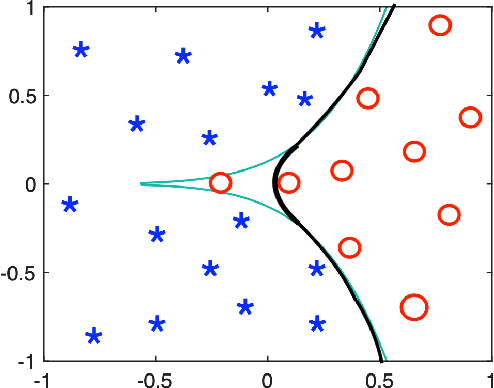
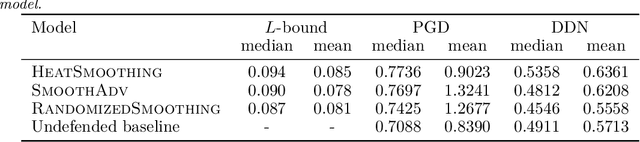
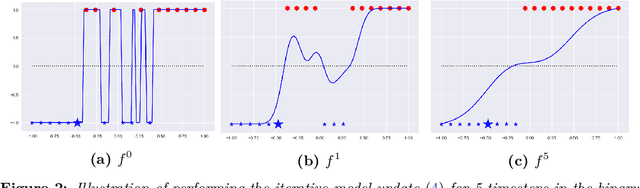
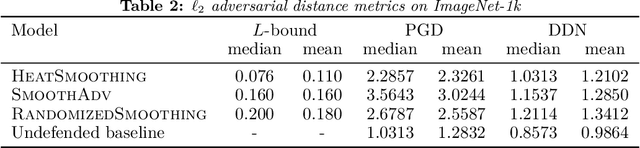
We present a deterministic method to compute the Gaussian average of neural networks used in regression and classification. Our method is based on an equivalence between training with a particular regularized loss, and the expected values of Gaussian averages. We use this equivalence to certify models which perform well on clean data but are not robust to adversarial perturbations. In terms of certified accuracy and adversarial robustness, our method is comparable to known stochastic methods such as randomized smoothing, but requires only a single model evaluation during inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge