Detection and Utilization of Reflections in LiDAR Scans Through Plane Optimization and Plane SLAM
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2024
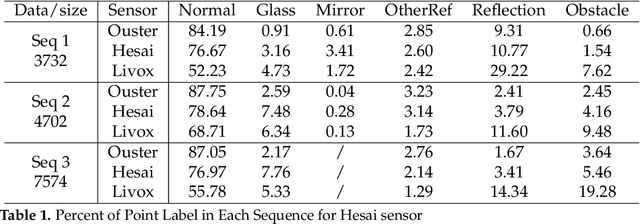

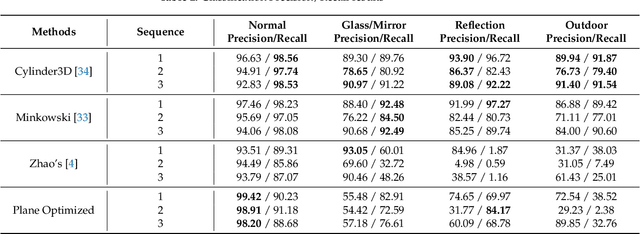
In LiDAR sensing, glass, mirrors and other material often cause inconsistent data readings, because the laser beams may report the distance of the glass, the distance of the object behind the glass or the distance to a reflected object. This causes problems in robotics and 3D reconstruction, especially with respect to localization, mapping and thus navigation. With dual-return LiDARs and other methods, one can detect the glass plane and classify the points in a single scan. In this work we go one step further and construct a global, optimized map of reflective planes, in order to then classify all LiDAR readings at the end. As our experiments will show, this approach provides superior classification accuracy compared to the single scan approach. The code and data for this work are available as open source online.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge