Detecting Driver's Distraction using Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2020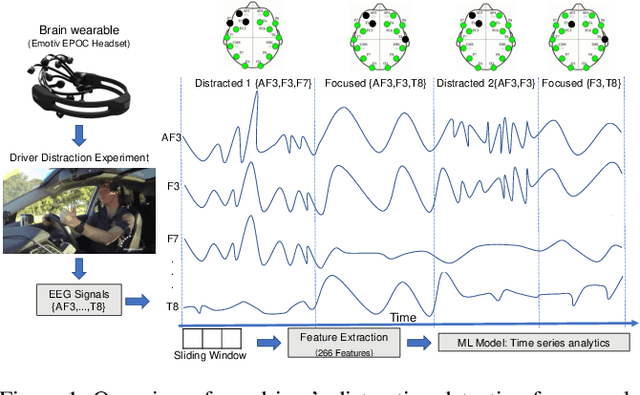
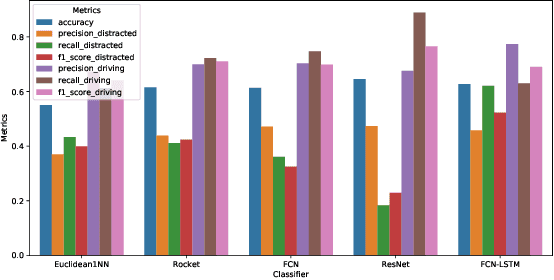
In this study we demonstrate a novel Brain Computer Interface (BCI) approach to detect driver distraction events to improve road safety. We use a commercial wireless headset that generates EEG signals from the brain. We collected real EEG signals from participants who undertook a 40-minute driving simulation and were required to perform different tasks while driving. These signals are segmented into short windows and labelled using a time series classification (TSC) model. We studied different TSC approaches and designed a Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network (LCRN) model for this task. Our results showed that our LRCN model performs better than the state of the art TSC models at detecting driver distraction events.
* 3 pages 2 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge