Dense 3D Visual Mapping via Semantic Simplification
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2019
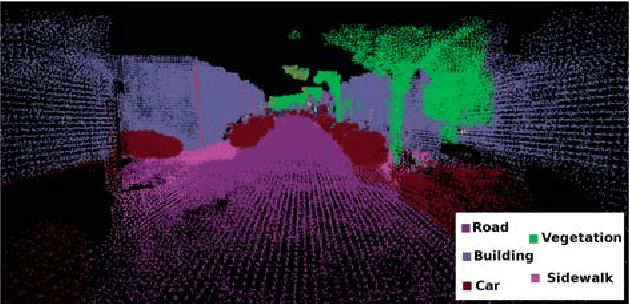
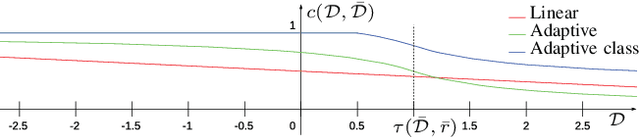
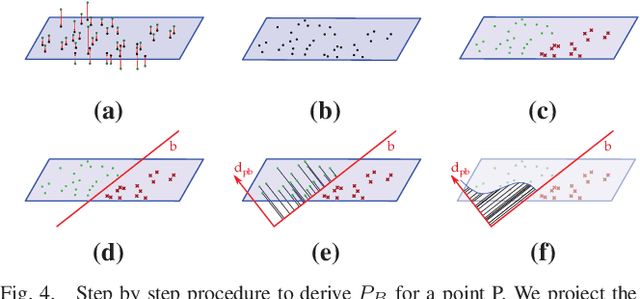
Dense 3D visual mapping estimates as many as possible pixel depths, for each image. This results in very dense point clouds that often contain redundant and noisy information, especially for surfaces that are roughly planar, for instance, the ground or the walls in the scene. In this paper we leverage on semantic image segmentation to discriminate which regions of the scene require simplification and which should be kept at high level of details. We propose four different point cloud simplification methods which decimate the perceived point cloud by relying on class-specific local and global statistics still maintaining more points in the proximity of class boundaries to preserve the infra-class edges and discontinuities. 3D dense model is obtained by fusing the point clouds in a 3D Delaunay Triangulation to deal with variable point cloud density. In the experimental evaluation we have shown that, by leveraging on semantics, it is possible to simplify the model and diminish the noise affecting the point clouds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge