Denoising Gravitational Waves with Enhanced Deep Recurrent Denoising Auto-Encoders
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2019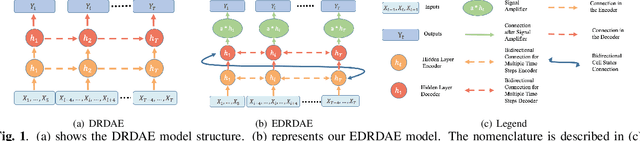
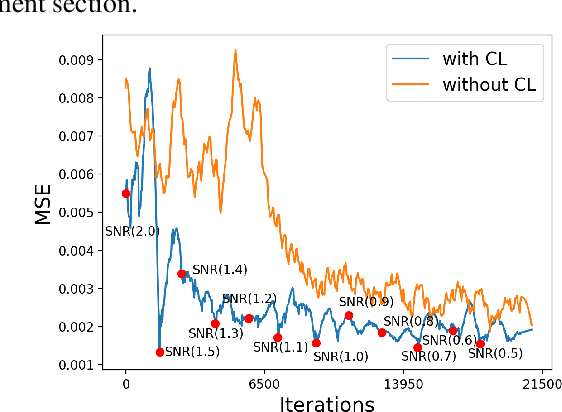
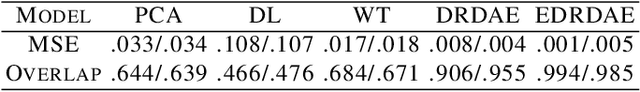
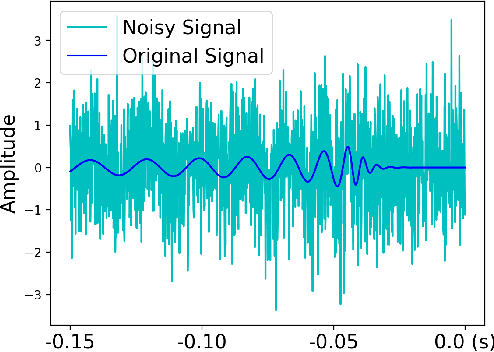
Denoising of time domain data is a crucial task for many applications such as communication, translation, virtual assistants etc. For this task, a combination of a recurrent neural net (RNNs) with a Denoising Auto-Encoder (DAEs) has shown promising results. However, this combined model is challenged when operating with low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) data embedded in non-Gaussian and non-stationary noise. To address this issue, we design a novel model, referred to as 'Enhanced Deep Recurrent Denoising Auto-Encoder' (EDRDAE), that incorporates a signal amplifier layer, and applies curriculum learning by first denoising high SNR signals, before gradually decreasing the SNR until the signals become noise dominated. We showcase the performance of EDRDAE using time-series data that describes gravitational waves embedded in very noisy backgrounds. In addition, we show that EDRDAE can accurately denoise signals whose topology is significantly more complex than those used for training, demonstrating that our model generalizes to new classes of gravitational waves that are beyond the scope of established denoising algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge