Defining and Characterizing Reward Hacking
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2022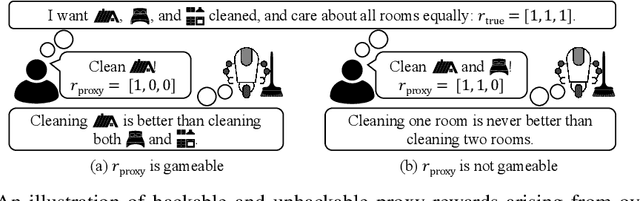

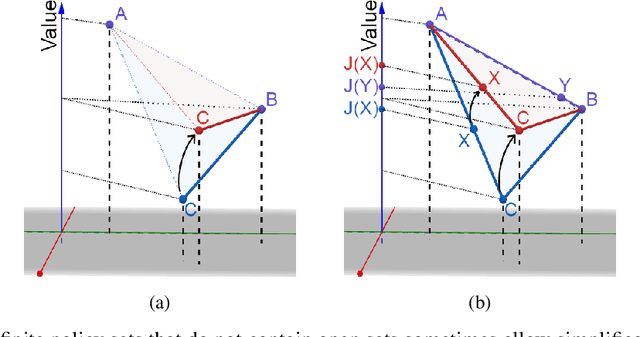
We provide the first formal definition of reward hacking, a phenomenon where optimizing an imperfect proxy reward function, $\mathcal{\tilde{R}}$, leads to poor performance according to the true reward function, $\mathcal{R}$. We say that a proxy is unhackable if increasing the expected proxy return can never decrease the expected true return. Intuitively, it might be possible to create an unhackable proxy by leaving some terms out of the reward function (making it "narrower") or overlooking fine-grained distinctions between roughly equivalent outcomes, but we show this is usually not the case. A key insight is that the linearity of reward (in state-action visit counts) makes unhackability a very strong condition. In particular, for the set of all stochastic policies, two reward functions can only be unhackable if one of them is constant. We thus turn our attention to deterministic policies and finite sets of stochastic policies, where non-trivial unhackable pairs always exist, and establish necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of simplifications, an important special case of unhackability. Our results reveal a tension between using reward functions to specify narrow tasks and aligning AI systems with human values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge