DeepPD: Joint Phase and Object Estimation from Phase Diversity with Neural Calibration of a Deformable Mirror
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2025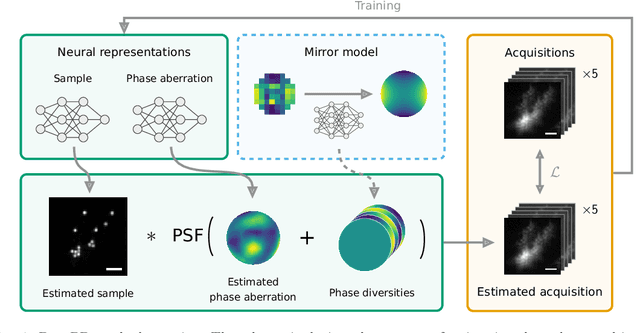
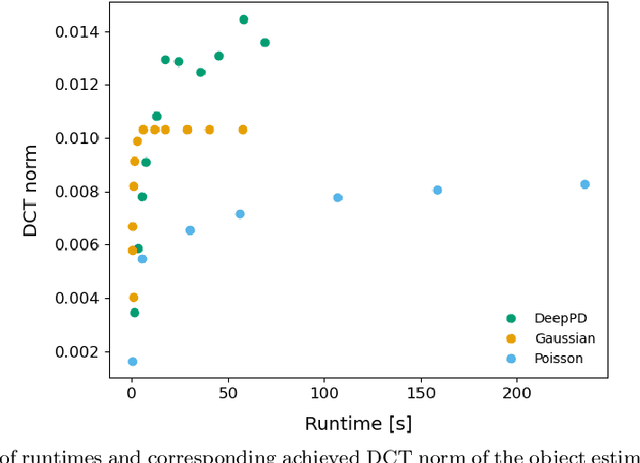


Sample-induced aberrations and optical imperfections limit the resolution of fluorescence microscopy. Phase diversity is a powerful technique that leverages complementary phase information in sequentially acquired images with deliberately introduced aberrations--the phase diversities--to enable phase and object reconstruction and restore diffraction-limited resolution. These phase diversities are typically introduced into the optical path via a deformable mirror. Existing phase-diversity-based methods are limited to Zernike modes, require large numbers of diversity images, or depend on accurate mirror calibration--which are all suboptimal. We present DeepPD, a deep learning-based framework that combines neural representations of the object and wavefront with a learned model of the deformable mirror to jointly estimate both object and phase from only five images. DeepPD improves robustness and reconstruction quality over previous approaches, even under severe aberrations. We demonstrate its performance on calibration targets and biological samples, including immunolabeled myosin in fixed PtK2 cells.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge