DeepGeo: Photo Localization with Deep Neural Network
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2018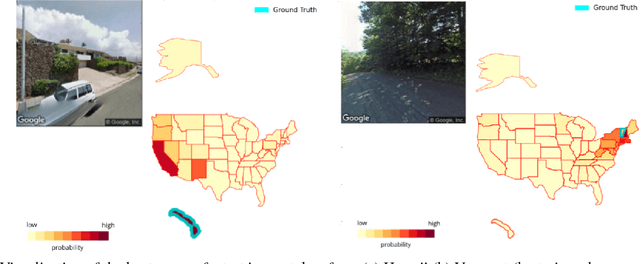
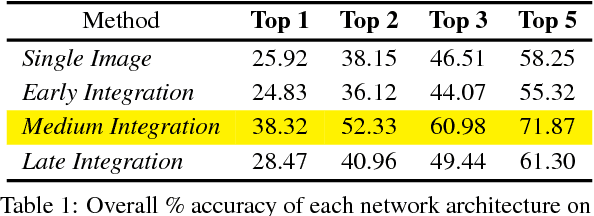

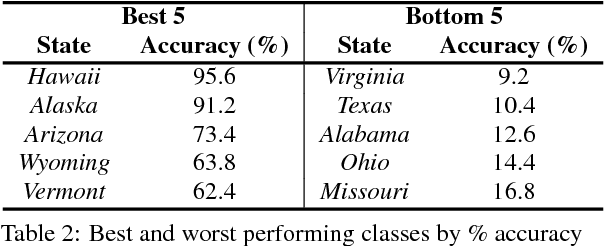
In this paper we address the task of determining the geographical location of an image, a pertinent problem in learning and computer vision. This research was inspired from playing GeoGuessr, a game that tests a humans' ability to localize themselves using just images of their surroundings. In particular, we wish to investigate how geographical, ecological and man-made features generalize for random location prediction. This is framed as a classification problem: given images sampled from the USA, the most-probable state among 50 is predicted. Previous work uses models extensively trained on large, unfiltered online datasets that are primed towards specific locations. To this end, we create (and open-source) the 50States10K dataset - with 0.5 million Google Street View images of the country. A deep neural network based on the ResNet architecture is trained, and four different strategies of incorporating low-level cardinality information are presented. This model achieves an accuracy 20 times better than chance on a test dataset, which rises to 71.87% when taking the best of top-5 guesses. The network also beats human subjects in 4 out of 5 rounds of GeoGuessr.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge