Deep Structured learning for mass segmentation from Mammograms
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2014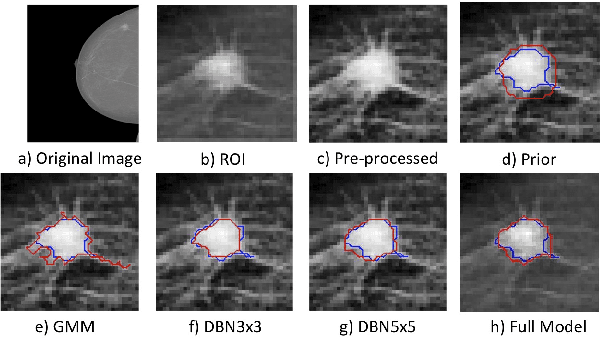
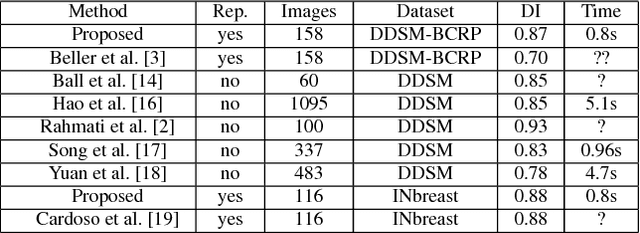
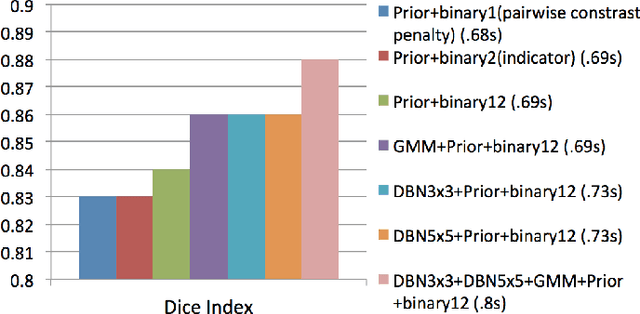
In this paper, we present a novel method for the segmentation of breast masses from mammograms exploring structured and deep learning. Specifically, using structured support vector machine (SSVM), we formulate a model that combines different types of potential functions, including one that classifies image regions using deep learning. Our main goal with this work is to show the accuracy and efficiency improvements that these relatively new techniques can provide for the segmentation of breast masses from mammograms. We also propose an easily reproducible quantitative analysis to as- sess the performance of breast mass segmentation methodologies based on widely accepted accuracy and running time measurements on public datasets, which will facilitate further comparisons for this segmentation problem. In particular, we use two publicly available datasets (DDSM-BCRP and INbreast) and propose the computa- tion of the running time taken for the methodology to produce a mass segmentation given an input image and the use of the Dice index to quantitatively measure the segmentation accuracy. For both databases, we show that our proposed methodology produces competitive results in terms of accuracy and running time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge