Deep Reinforcement Learning for Entity Alignment
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2022
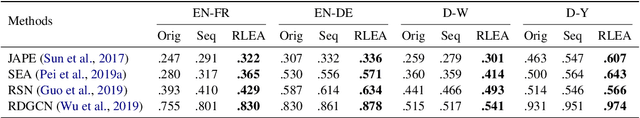


Embedding-based methods have attracted increasing attention in recent entity alignment (EA) studies. Although great promise they can offer, there are still several limitations. The most notable is that they identify the aligned entities based on cosine similarity, ignoring the semantics underlying the embeddings themselves. Furthermore, these methods are shortsighted, heuristically selecting the closest entity as the target and allowing multiple entities to match the same candidate. To address these limitations, we model entity alignment as a sequential decision-making task, in which an agent sequentially decides whether two entities are matched or mismatched based on their representation vectors. The proposed reinforcement learning (RL)-based entity alignment framework can be flexibly adapted to most embedding-based EA methods. The experimental results demonstrate that it consistently advances the performance of several state-of-the-art methods, with a maximum improvement of 31.1% on Hits@1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge