Deep Neural Networks for Approximating Stream Reasoning with C-SPARQL
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2021
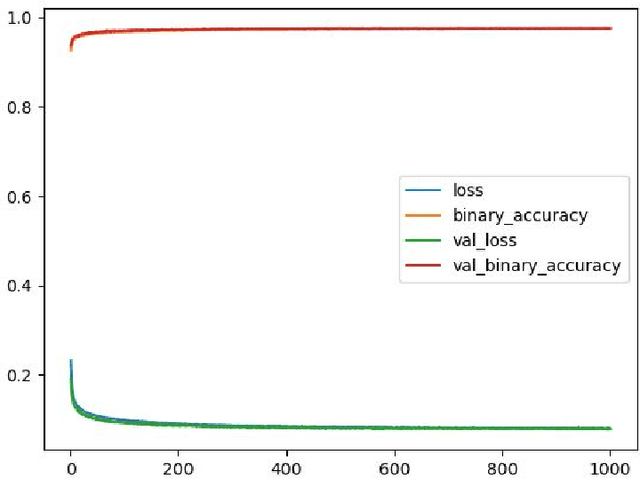
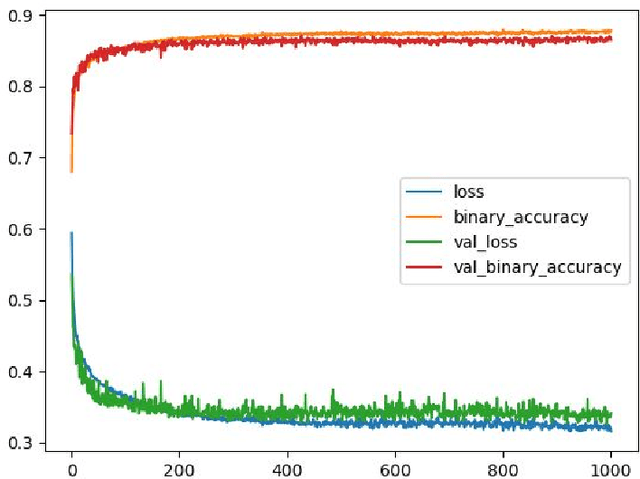
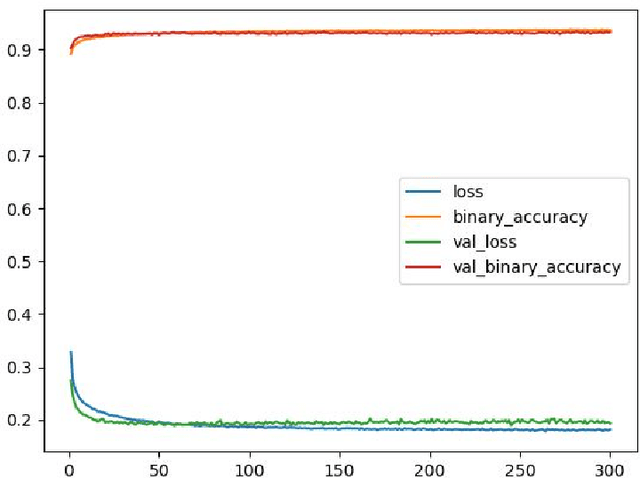
The amount of information produced, whether by newspapers, blogs and social networks, or by monitoring systems, is increasing rapidly. Processing all this data in real-time, while taking into consideration advanced knowledge about the problem domain, is challenging, but required in scenarios where assessing potential risks in a timely fashion is critical. C-SPARQL, a language for continuous queries over streams of RDF data, is one of the more prominent approaches in stream reasoning that provides such continuous inference capabilities over dynamic data that go beyond mere stream processing. However, it has been shown that, in the presence of huge amounts of data, C-SPARQL may not be able to answer queries in time, in particular when the frequency of incoming data is higher than the time required for reasoning with that data. In this paper, we investigate whether reasoning with C-SPARQL can be approximated using Recurrent Neural Networks and Convolutional Neural Networks, two neural network architectures that have been shown to be well-suited for time series forecasting and time series classification, to leverage on their higher processing speed once the network has been trained. We consider a variety of different kinds of queries and obtain overall positive results with high accuracies while improving processing time often by several orders of magnitude.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge