Deep Neural Imputation: A Framework for Recovering Incomplete Brain Recordings
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2022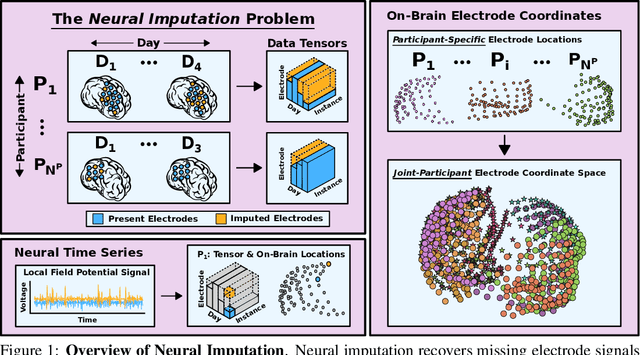
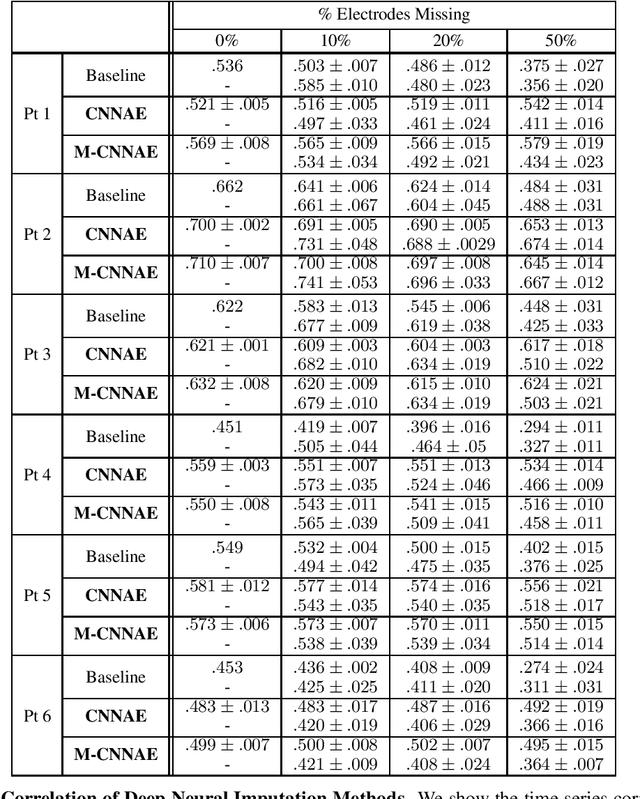
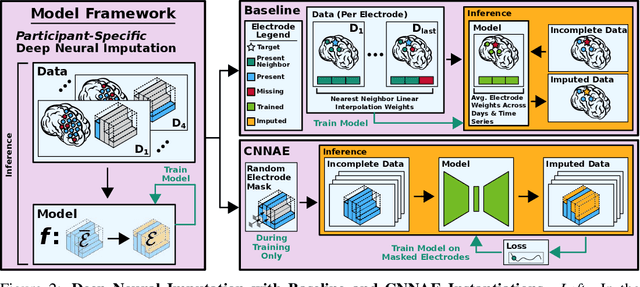
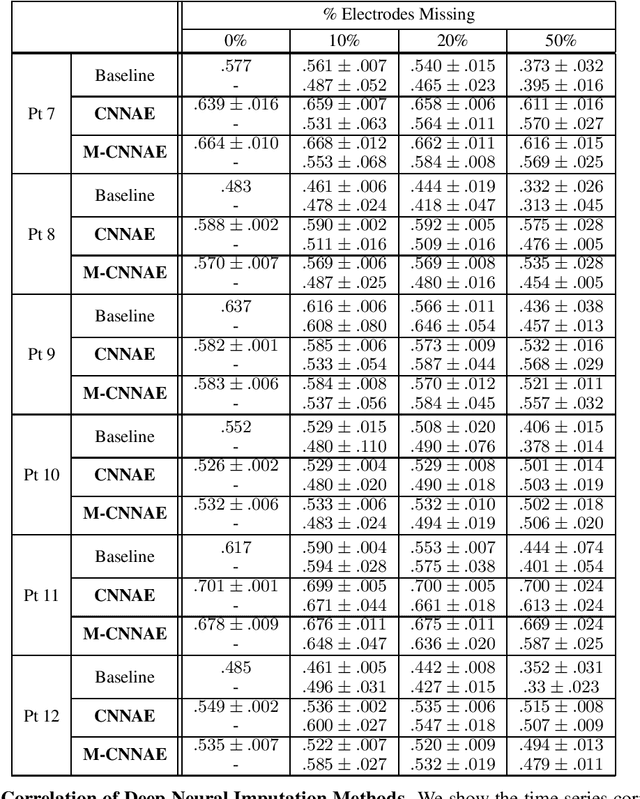
Neuroscientists and neuroengineers have long relied on multielectrode neural recordings to study the brain. However, in a typical experiment, many factors corrupt neural recordings from individual electrodes, including electrical noise, movement artifacts, and faulty manufacturing. Currently, common practice is to discard these corrupted recordings, reducing already limited data that is difficult to collect. To address this challenge, we propose Deep Neural Imputation (DNI), a framework to recover missing values from electrodes by learning from data collected across spatial locations, days, and participants. We explore our framework with a linear nearest-neighbor approach and two deep generative autoencoders, demonstrating DNI's flexibility. One deep autoencoder models participants individually, while the other extends this architecture to model many participants jointly. We evaluate our models across 12 human participants implanted with multielectrode intracranial electrocorticography arrays; participants had no explicit task and behaved naturally across hundreds of recording hours. We show that DNI recovers not only time series but also frequency content, and further establish DNI's practical value by recovering significant performance on a scientifically-relevant downstream neural decoding task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge