Deep Metric Learning with Hierarchical Triplet Loss
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2018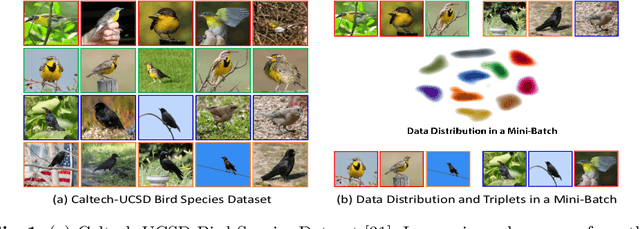
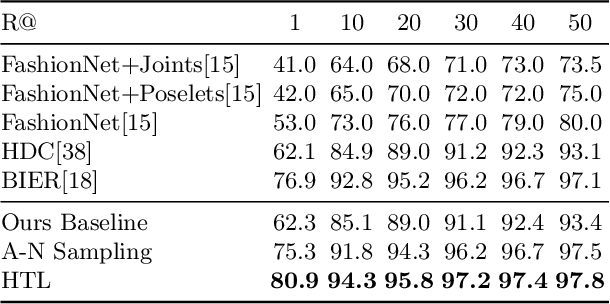
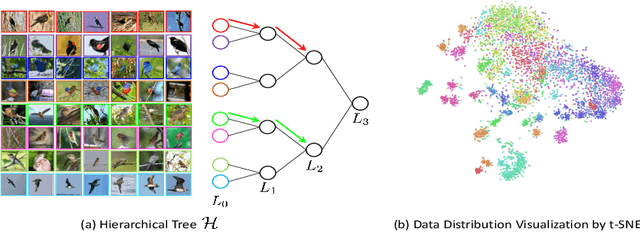
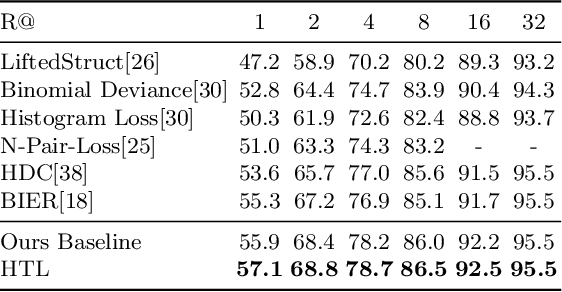
We present a novel hierarchical triplet loss (HTL) capable of automatically collecting informative training samples (triplets) via a defined hierarchical tree that encodes global context information. This allows us to cope with the main limitation of random sampling in training a conventional triplet loss, which is a central issue for deep metric learning. Our main contributions are two-fold. (i) we construct a hierarchical class-level tree where neighboring classes are merged recursively. The hierarchical structure naturally captures the intrinsic data distribution over the whole database. (ii) we formulate the problem of triplet collection by introducing a new violate margin, which is computed dynamically based on the designed hierarchical tree. This allows it to automatically select meaningful hard samples with the guide of global context. It encourages the model to learn more discriminative features from visual similar classes, leading to faster convergence and better performance. Our method is evaluated on the tasks of image retrieval and face recognition, where it outperforms the standard triplet loss substantially by 1%-18%. It achieves new state-of-the-art performance on a number of benchmarks, with much fewer learning iterations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge