Deep Learning for Individual Heterogeneity
Paper and Code
Oct 28, 2020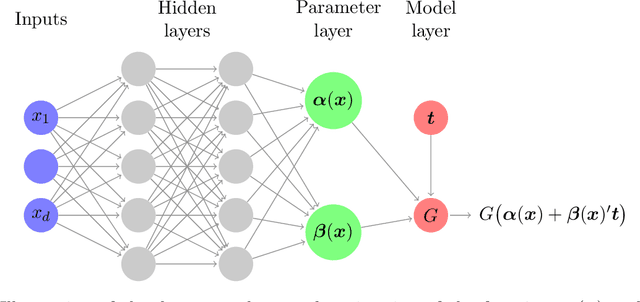


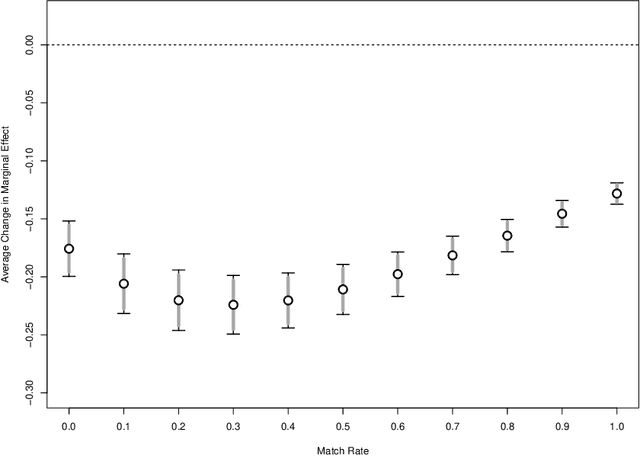
We propose a methodology for effectively modeling individual heterogeneity using deep learning while still retaining the interpretability and economic discipline of classical models. We pair a transparent, interpretable modeling structure with rich data environments and machine learning methods to estimate heterogeneous parameters based on potentially high dimensional or complex observable characteristics. Our framework is widely-applicable, covering numerous settings of economic interest. We recover, as special cases, well-known examples such as average treatment effects and parametric components of partially linear models. However, we also seamlessly deliver new results for diverse examples such as price elasticities, willingness-to-pay, and surplus measures in choice models, average marginal and partial effects of continuous treatment variables, fractional outcome models, count data, heterogeneous production function components, and more. Deep neural networks are well-suited to structured modeling of heterogeneity: we show how the network architecture can be designed to match the global structure of the economic model, giving novel methodology for deep learning as well as, more formally, improved rates of convergence. Our results on deep learning have consequences for other structured modeling environments and applications, such as for additive models. Our inference results are based on an influence function we derive, which we show to be flexible enough to to encompass all settings with a single, unified calculation, removing any requirement for case-by-case derivations. The usefulness of the methodology in economics is shown in two empirical applications: the response of 410(k) participation rates to firm matching and the impact of prices on subscription choices for an online service. Extensions to instrumental variables and multinomial choices are shown.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge