Deep Learning for Automated Screening of Tuberculosis from Indian Chest X-rays: Analysis and Update
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2020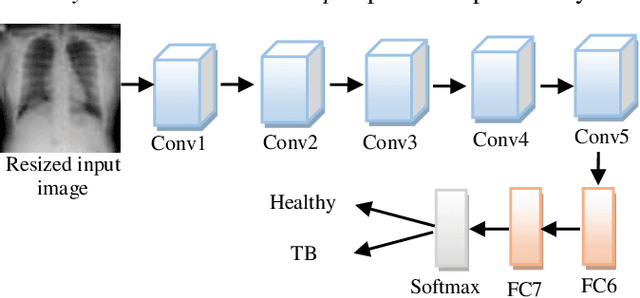
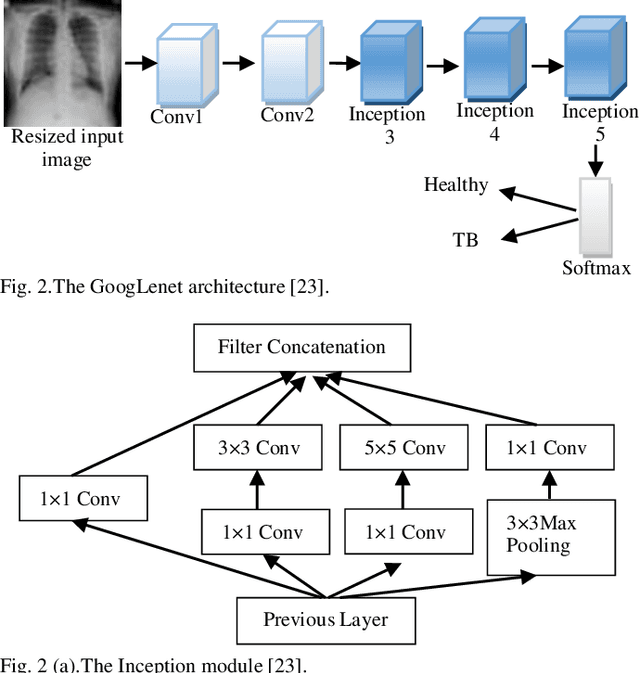
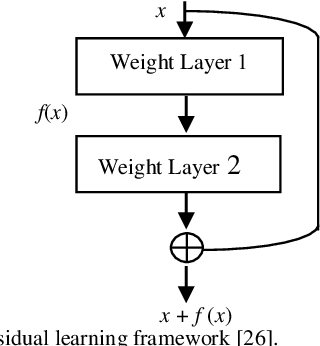
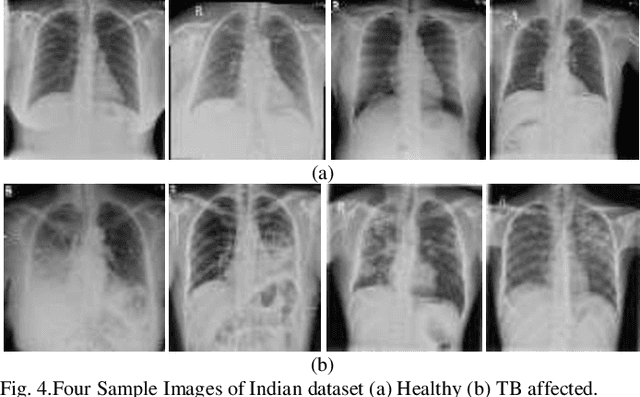
Background and Objective: Tuberculosis (TB) is a significant public health issue and a leading cause of death worldwide. Millions of deaths can be averted by early diagnosis and successful treatment of TB patients. Automated diagnosis of TB holds vast potential to assist medical experts in expediting and improving its diagnosis, especially in developing countries like India, where there is a shortage of trained medical experts and radiologists. To date, several deep learning based methods for automated detection of TB from chest radiographs have been proposed. However, the performance of a few of these methods on the Indian chest radiograph data set has been suboptimal, possibly due to different texture of the lungs on chest radiographs of Indian subjects compared to other countries. Thus deep learning for accurate and automated diagnosis of TB on Indian datasets remains an important subject of research. Methods: The proposed work explores the performance of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the diagnosis of TB in Indian chest x-ray images. Three different pre-trained neural network models, AlexNet, GoogLenet, and ResNet are used to classify chest x-ray images into healthy or TB infected. The proposed approach does not require any pre-processing technique. Also, other works use pre-trained NNs as a tool for crafting features and then apply standard classification techniques. However, we attempt an end to end NN model based diagnosis of TB from chest x-rays. The proposed visualization tool can also be used by radiologists in the screening of large datasets. Results: The proposed method achieved 93.40% accuracy with 98.60% sensitivity to diagnose TB for the Indian population. Conclusions: The performance of the proposed method is also tested against techniques described in the literature. The proposed method outperforms the state of art on Indian and Shenzhen datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge