Deep Imbalanced Regression to Estimate Vascular Age from PPG Data: a Novel Digital Biomarker for Cardiovascular Health
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2024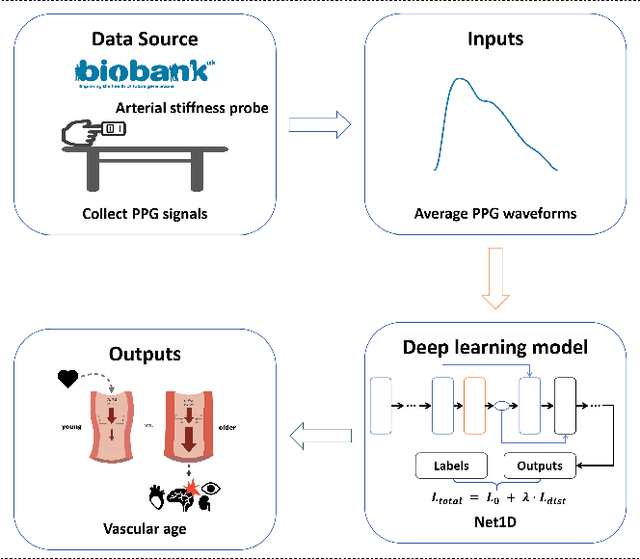
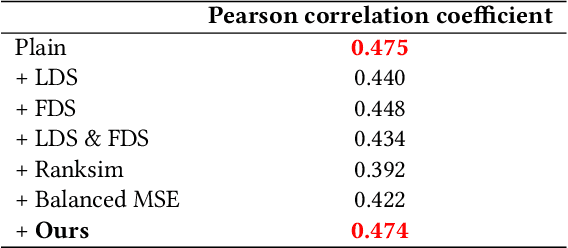
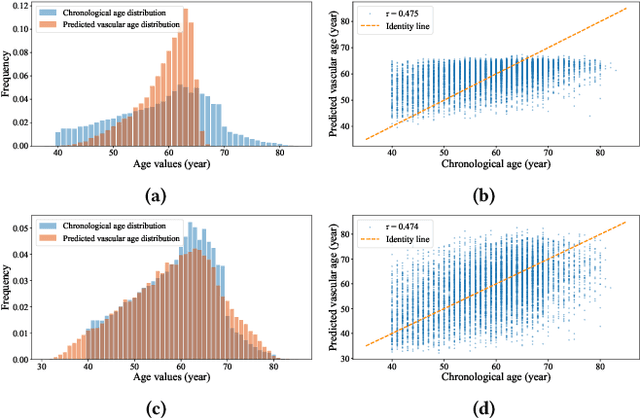
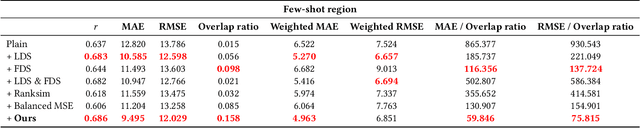
Photoplethysmography (PPG) is emerging as a crucial tool for monitoring human hemodynamics, with recent studies highlighting its potential in assessing vascular aging through deep learning. However, real-world age distributions are often imbalanced, posing significant challenges for deep learning models. In this paper, we introduce a novel, simple, and effective loss function named the Dist Loss to address deep imbalanced regression tasks. We trained a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (Net1D) incorporating the Dist Loss on the extensive UK Biobank dataset (n=502,389) to estimate vascular age from PPG signals and validate its efficacy in characterizing cardiovascular health. The model's performance was validated on a 40% held-out test set, achieving state-of-the-art results, especially in regions with small sample sizes. Furthermore, we divided the population into three subgroups based on the difference between predicted vascular age and chronological age: less than -10 years, between -10 and 10 years, and greater than 10 years. We analyzed the relationship between predicted vascular age and several cardiovascular events over a follow-up period of up to 10 years, including death, coronary heart disease, and heart failure. Our results indicate that the predicted vascular age has significant potential to reflect an individual's cardiovascular health status. Our code will be available at https://github.com/Ngk03/AI-vascular-age.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge