Deceptive Decision-Making Under Uncertainty
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2021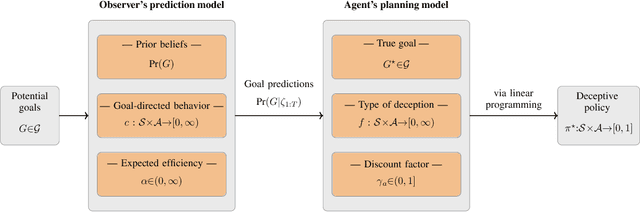
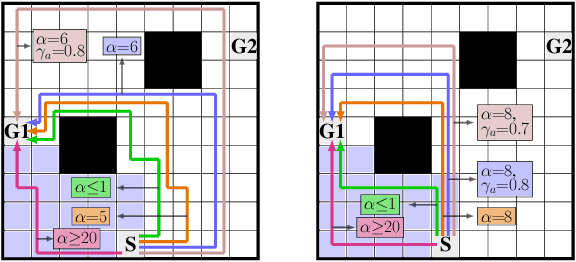
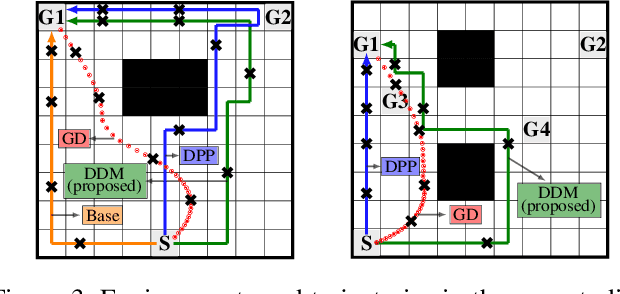
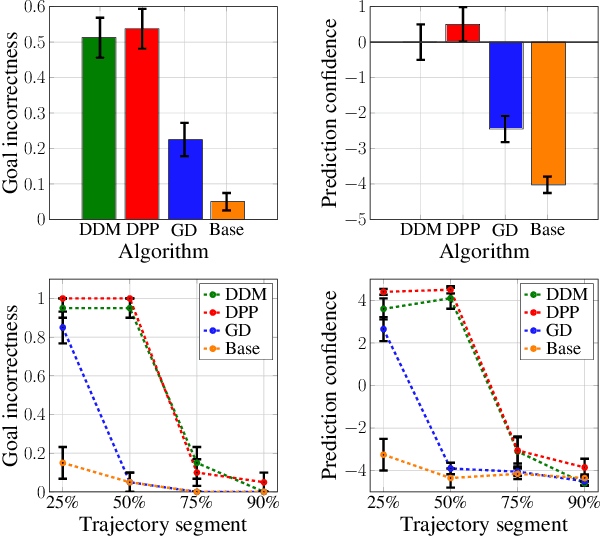
We study the design of autonomous agents that are capable of deceiving outside observers about their intentions while carrying out tasks in stochastic, complex environments. By modeling the agent's behavior as a Markov decision process, we consider a setting where the agent aims to reach one of multiple potential goals while deceiving outside observers about its true goal. We propose a novel approach to model observer predictions based on the principle of maximum entropy and to efficiently generate deceptive strategies via linear programming. The proposed approach enables the agent to exhibit a variety of tunable deceptive behaviors while ensuring the satisfaction of probabilistic constraints on the behavior. We evaluate the performance of the proposed approach via comparative user studies and present a case study on the streets of Manhattan, New York, using real travel time distributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge