Decentralized Collaborative Learning Framework with External Privacy Leakage Analysis
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2024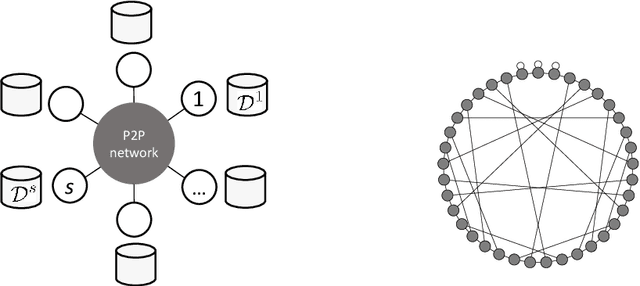
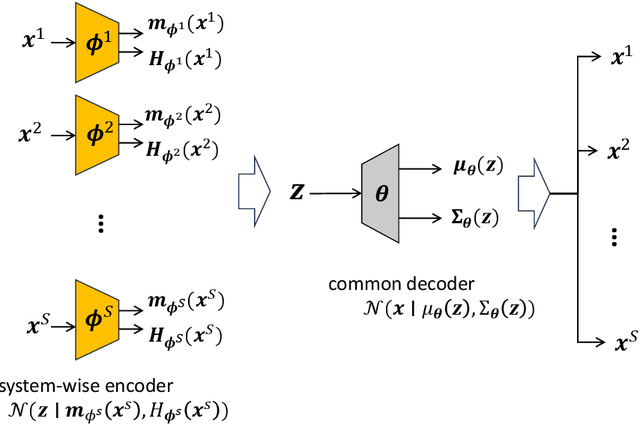
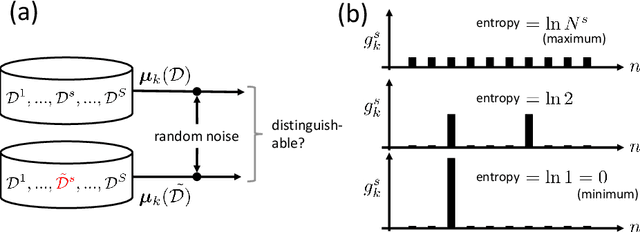
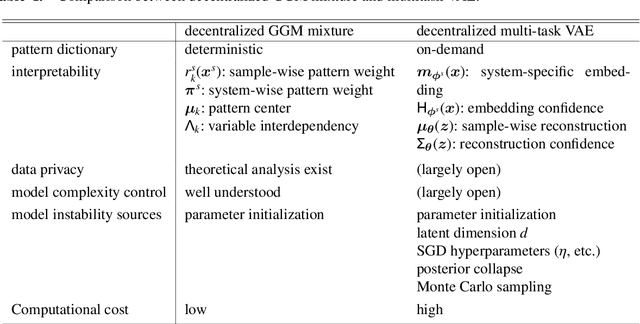
This paper presents two methodological advancements in decentralized multi-task learning under privacy constraints, aiming to pave the way for future developments in next-generation Blockchain platforms. First, we expand the existing framework for collaborative dictionary learning (CollabDict), which has previously been limited to Gaussian mixture models, by incorporating deep variational autoencoders (VAEs) into the framework, with a particular focus on anomaly detection. We demonstrate that the VAE-based anomaly score function shares the same mathematical structure as the non-deep model, and provide comprehensive qualitative comparison. Second, considering the widespread use of "pre-trained models," we provide a mathematical analysis on data privacy leakage when models trained with CollabDict are shared externally. We show that the CollabDict approach, when applied to Gaussian mixtures, adheres to a Renyi differential privacy criterion. Additionally, we propose a practical metric for monitoring internal privacy breaches during the learning process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge