Debiasing 6-DOF IMU via Hierarchical Learning of Continuous Bias Dynamics
Paper and Code
Apr 13, 2025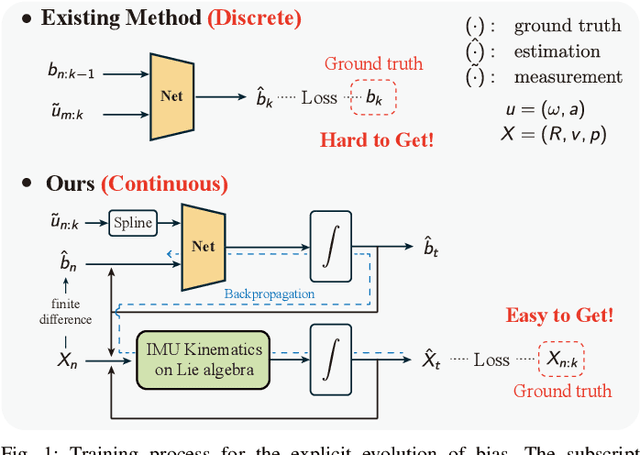
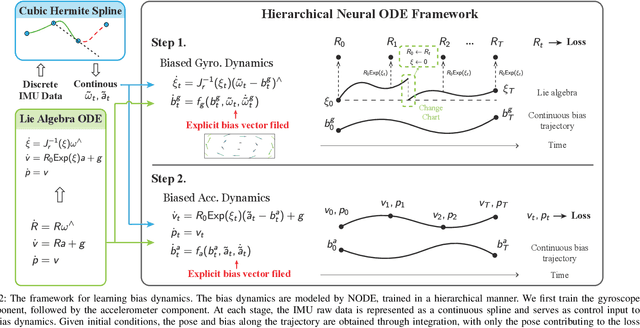
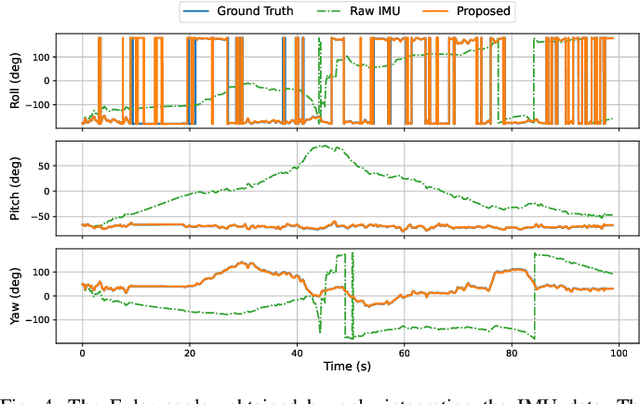
This paper develops a deep learning approach to the online debiasing of IMU gyroscopes and accelerometers. Most existing methods rely on implicitly learning a bias term to compensate for raw IMU data. Explicit bias learning has recently shown its potential as a more interpretable and motion-independent alternative. However, it remains underexplored and faces challenges, particularly the need for ground truth bias data, which is rarely available. To address this, we propose a neural ordinary differential equation (NODE) framework that explicitly models continuous bias dynamics, requiring only pose ground truth, often available in datasets. This is achieved by extending the canonical NODE framework to the matrix Lie group for IMU kinematics with a hierarchical training strategy. The validation on two public datasets and one real-world experiment demonstrates significant accuracy improvements in IMU measurements, reducing errors in both pure IMU integration and visual-inertial odometry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge