DEAL: Decoupled Classifier with Adaptive Linear Modulation for Group Robust Early Diagnosis of MCI to AD Conversion
Paper and Code
Nov 25, 2024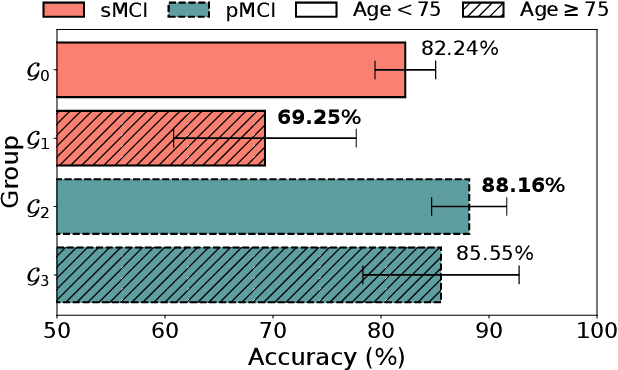


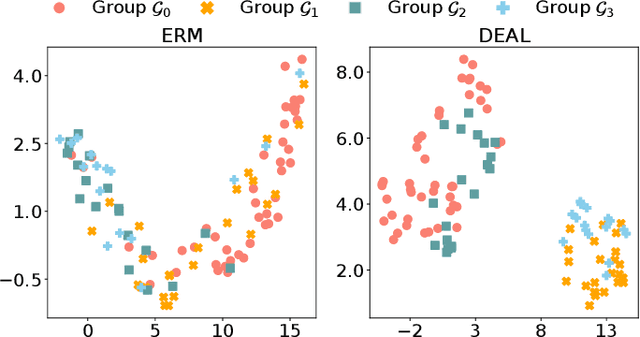
While deep learning-based Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnosis has recently made significant advancements, particularly in predicting the conversion of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD based on MRI images, there remains a critical gap in research regarding the group robustness of the diagnosis. Although numerous studies pointed out that deep learning-based classifiers may exhibit poor performance in certain groups by relying on unimportant attributes, this issue has been largely overlooked in the early diagnosis of MCI to AD conversion. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive investigation of the group robustness in the early diagnosis of MCI to AD conversion using MRI images, focusing on disparities in accuracy between groups, specifically sMCI and pMCI individuals divided by age. Our experiments reveal that standard classifiers consistently underperform for certain groups across different architectures, highlighting the need for more tailored approaches. To address this, we propose a novel method, dubbed DEAL (DEcoupled classifier with Adaptive Linear modulation), comprising two key components: (1) a linear modulation of features from the penultimate layer, incorporating easily obtainable age and cognitive indicative tabular features, and (2) a decoupled classifier that provides more tailored decision boundaries for each group, further improving performance. Through extensive experiments and evaluations across different architectures, we demonstrate the efficacy of DEAL in improving the group robustness of the MCI to AD conversion prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge