Data Selection for Fine-tuning Large Language Models Using Transferred Shapley Values
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2023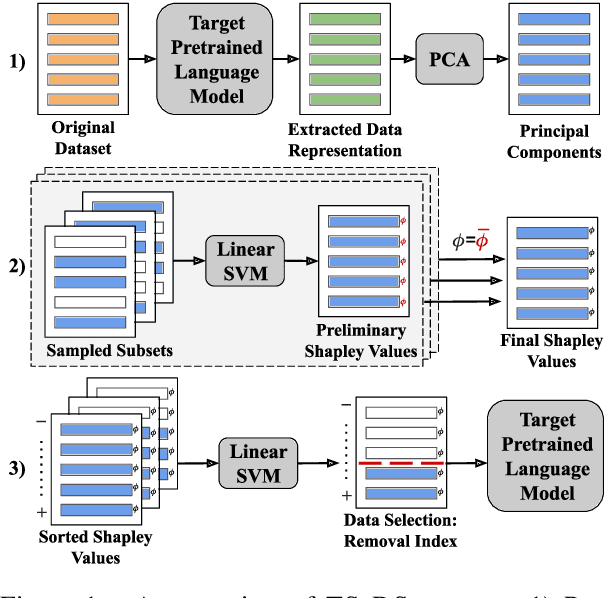
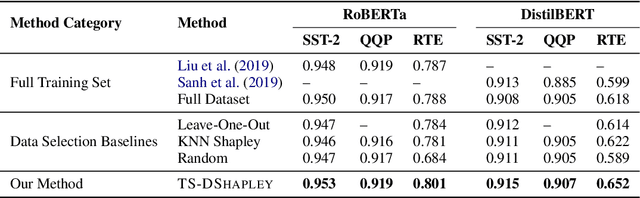
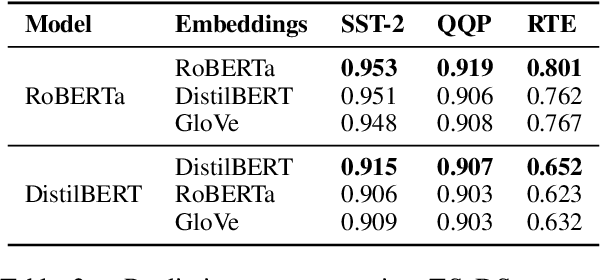
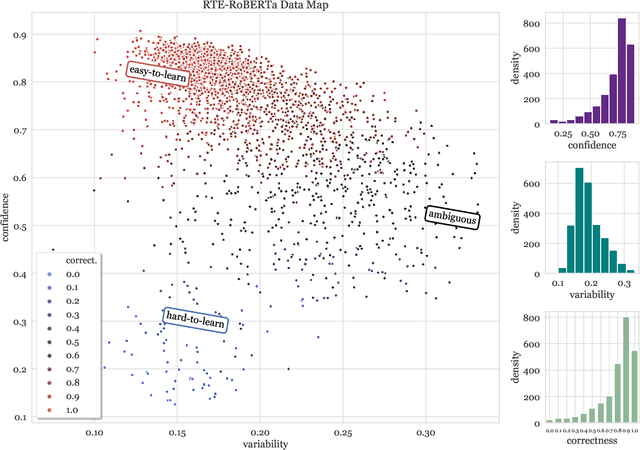
Although Shapley values have been shown to be highly effective for identifying harmful training instances, dataset size and model complexity constraints limit the ability to apply Shapley-based data valuation to fine-tuning large pre-trained language models. To address this, we propose TS-DShapley, an algorithm that reduces computational cost of Shapley-based data valuation through: 1) an efficient sampling-based method that aggregates Shapley values computed from subsets for valuation of the entire training set, and 2) a value transfer method that leverages value information extracted from a simple classifier trained using representations from the target language model. Our experiments applying TS-DShapley to select data for fine-tuning BERT-based language models on benchmark natural language understanding (NLU) datasets show that TS-DShapley outperforms existing data selection methods. Further, TS-DShapley can filter fine-tuning data to increase language model performance compared to training with the full fine-tuning dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge