Data Programming using Continuous and Quality-Guided Labeling Functions
Paper and Code
Nov 22, 2019
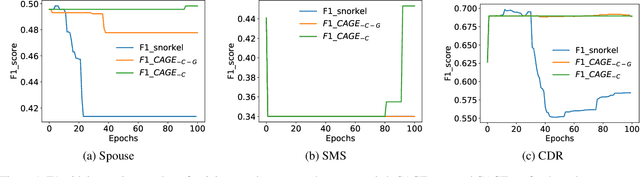

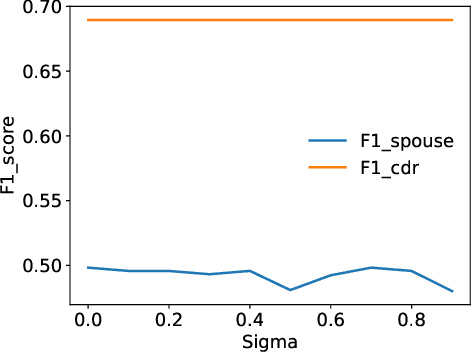
Scarcity of labeled data is a bottleneck for supervised learning models. A paradigm that has evolved for dealing with this problem is data programming. An existing data programming paradigm allows human supervision to be provided as a set of discrete labeling functions (LF) that output possibly noisy labels to input instances and a generative modelfor consolidating the weak labels. We enhance and generalize this paradigm by supporting functions that output a continuous score (instead of a hard label) that noisily correlates with labels. We show across five applications that continuous LFs are more natural to program and lead to improved recall. We also show that accuracy of existing generative models is unstable with respect to initialization, training epochs, and learning rates. We give control to the data programmer to guide the training process by providing intuitive quality guides with each LF. We propose an elegant method of incorporating these guides into the generative model. Our overall method, called CAGE, makes the data programming paradigm more reliable than other tricks based on initialization, sign-penalties, or soft-accuracy constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge